Combination therapy with anti-ErbB3 monoclonal antibodies and EGFR TKIs potently inhibits non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 23896512
- PMCID: PMC3787155
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.1141
Combination therapy with anti-ErbB3 monoclonal antibodies and EGFR TKIs potently inhibits non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
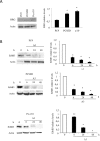
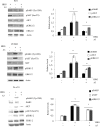
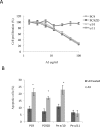
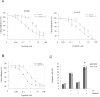
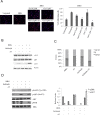
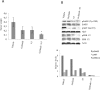
Personalized therapy of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been improved by the introduction of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), gefitinib and erlotinib. EGFR TKIs induce dramatic objective responses and increase survival in patients bearing sensitizing mutations in the EGFR intracytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. However, virtually all patients develop resistance, and this is responsible for disease relapse. Hence several efforts are being undertaken to understand the mechanisms of resistance in order to develop combination treatments capable to sensitize resistant cells to EGFR TKIs. Recent studies have suggested that upregulation of another member of the EGFR receptor family, namely ErbB3 is involved in drug resistance, through increased phosphorylation of its intracytoplasmic domain and activation of PI3K/AKT signaling. In this paper we first show, by using a set of malignant pleural effusion derived cell cultures (MPEDCC) from patients with lung adenocarcinoma, that surface ErbB3 expression correlates with increased AKT phosphorylation. Antibodies against ErbB3, namely A3, which we previously demonstrated to induce receptor internalization and degradation, inhibit growth and induce apoptosis only in cells overexpressing surface ErbB3. Furthermore, combination of anti-ErbB3 antibodies with EGFR TKIs synergistically affect cell proliferation in vitro, cause cell cycle arrest, up-regulate p21 expression and inhibit tumor growth in mouse xenografts. Importantly, potentiation of gefitinib by anti-ErbB3 antibodies occurs both in de novo and in ab initio resistant cells. Anti-ErbB3 mAbs strongly synergize also with the dual EGFR and HER2 inhibitor lapatinib. Our results suggest that combination treatment with EGFR TKI and antibodies against ErbB3 should be a promising approach to pursue in the clinic.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Heffernan KS, Wanke CA, Dong K, Warner PJ, Anskat PE, Karas RH, Kuvin JT. Lung cancer stem cells: tumor biology and clinical implications. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2012;8:217–22. - PubMed
-
- Saintigny P, Burger JA. Recent advances in non-small cell lung cancer biology and clinical management. Discov Med. 2012;13:287–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

