Antidiarrheal activity of 19-deoxyicetexone isolated from Salvia ballotiflora Benth in mice and rats
- PMID: 23896615
- PMCID: PMC6270266
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules18088895
Antidiarrheal activity of 19-deoxyicetexone isolated from Salvia ballotiflora Benth in mice and rats
Abstract
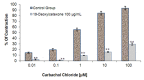
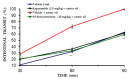
The antidiarrheal properties of 19-deoxyicetexone, a diterpenoid isolated from Salvia ballotiflora were evaluated on castor oil-, arachidonic acid (AA)- and prostaglandin (PGE₂)-induced diarrhea in rodent models. The structure of 19-deoxyicetexone was determined by X-ray crystallography, mass spectrometry (EI-MS), as well as ultraviolet (UV-Vis), infrared (FT-IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopies. This compound significantly and dose-dependently reduced frequency of stooling in castor oil-induced diarrhea, and at dose of 25 mg/kg it also inhibited diarrhea induced with AA, while it had no effect on PGE₂-induced diarrhea. This compound at doses of 25 mg/kg also diminished castor oil-induced enteropooling and intestinal motility, and inhibited the contraction of the rats' ileum induced by carbachol chloride at a concentration of 100 µg/mL. 19-Deoxyicetexone did not present acute toxicity at doses of 625 mg/kg. Its antidiarrheal activity may be due to increased reabsorption of NaCl and water and inhibition of the release of prostaglandins, gastrointestinal motility and fluid accumulation in the intestinal tracts of rats. These findings suggest that 19-deoxyicetexone may be used in the treatment of diarrhea, although more studies must be carried out to confirm this.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antidiarrheal activity of cashew GUM, a complex heteropolysaccharide extracted from exudate of Anacardium occidentale L. in rodents.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Nov 4;174:299-307. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.020. Epub 2015 Aug 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26297843
-
Antidiarrheal activity of Pyrenacantha staudtii Engl. (Icacinaceae) aqueous leaf extract in rodents.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Sep 1;137(1):148-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.04.068. Epub 2011 May 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21571058
-
Freeze dried extracts of Bidens biternata (Lour.) Merr. and Sheriff. show significant antidiarrheal activity in in-vivo models of diarrhea.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Dec 4;193:416-422. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.09.041. Epub 2016 Sep 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27664442
-
Evaluation of the anti-diarrheal activity of Salvia connivens.Pharm Biol. 2014 Nov;52(11):1467-70. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2014.898076. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Pharm Biol. 2014. PMID: 25026354
-
Antidiarrheal evaluation of the ethanol extract of Nauclea latifolia root bark.Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;32(8):551-5. doi: 10.1358/mf.2010.32.8.1440747. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 21132124
Cited by
-
A Review on the Ethnopharmacology and Phytochemistry of the Neotropical Sages (Salvia Subgenus Calosphace; Lamiaceae) Emphasizing Mexican Species.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 19;13:867892. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.867892. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35517814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental assessment of antidiarrheal and antisecretory activity of 80% methanolic leaf extract of Zehneria scabra in mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 2;14:460. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-460. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25465058 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, Absolute Configuration, and Antiproliferative Activity of Abietane and Icetexane Diterpenoids from Salvia ballotiflora.Molecules. 2017 Oct 18;22(10):1690. doi: 10.3390/molecules22101690. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29057832 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiarrheal activity of crude methanolic root extract of Idigofera spicata Forssk.(Fabaceae).BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Aug 5;16:272. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1252-4. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27492007 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Galla Chinensis Oral Solution as well as Its Stability, Safety, and Antidiarrheal Activity Evaluation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:1851459. doi: 10.1155/2017/1851459. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28811824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Water and Sanitation. Volume 12 WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 1996.
-
- Hardman J.G., Limbird L.E. Goodman and Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. McGraw Hill; New York, NY, USA: 2010. pp. 914–931.
-
- Kumar S., Garg V.K., Kumar N., Sharma P.K., Chaudhary S., Upadhyay A. Pharmacognostical studies on the leaves of Ziziphus nummularia (Burm. F.) Eur. J. Exper. Biol. 2011;1:77–83.
-
- Beverly C.D., Sudarsanam G. Ethnomedicinal plant knowledge and practice of people of Javadhu hills in Tamilnadu. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011;1:S79–S81. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(11)60129-9. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

