Inhibitors of urokinase type plasminogen activator and cytostatic activity from crude plants extracts
- PMID: 23896619
- PMCID: PMC4034058
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules18088945
Inhibitors of urokinase type plasminogen activator and cytostatic activity from crude plants extracts
Abstract
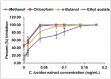
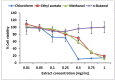
In view of the clear evidence that urokinase type plasminogen activator (uPA) plays an important role in the processes of tumor cell metastasis, aortic aneurysm, and multiple sclerosis, it has become a target of choice for pharmacological intervention. The goal of this study was thus to determine the presence of inhibitors of uPA in plants known traditionally for their anti-tumor properties. Crude methanol extracts were prepared from the leaves of plants (14) collected from the subtropical dry forest (Guanica, Puerto Rico), and tested for the presence of inhibitors of uPA using the fibrin plate assay. The extracts that tested positive (6) were then partitioned with petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate and n-butanol, in a sequential manner. The resulting fractions were then tested again using the fibrin plate assay. Extracts from leaves of Croton lucidus (C. lucidus) showed the presence of a strong uPA inhibitory activity. Serial dilutions of these C. lucidus partitions were performed to determine the uPA inhibition IC₅₀ values. The chloroform extract showed the lowest IC₅₀ value (3.52 µg/mL) and hence contained the most potent uPA inhibitor. Further investigations revealed that the crude methanol extract and its chloroform and n-butanol partitions did not significantly inhibit closely related proteases such as the tissue type plasminogen activator (tPA) and plasmin, indicating their selectivity for uPA, and hence superior potential for medicinal use with fewer side effects. In a further evaluation of their therapeutic potential for prevention of cancer metastasis, the C. lucidus extracts displayed cytostatic activity against human pancreatic carcinoma (PaCa-2) cells, as determined through an MTS assay. The cytostatic activities recorded for each of the partitions correlated with their relative uPA inhibitory activities. There are no existing reports of uPA inhibitors being present in any of the plants reported in this study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The complex between urokinase plasminogen activator and its type-1 inhibitor in breast cancer extracts quantitated by ELISA.J Immunol Methods. 1997 Apr 11;203(1):55-65. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(97)00008-2. J Immunol Methods. 1997. PMID: 9134030
-
Inhibition of plasminogen activation protects against ganglion cell loss in a mouse model of retinal damage.Mol Vis. 2003 Jun 12;9:238-48. Mol Vis. 2003. PMID: 12813409
-
Single-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator does not possess measurable intrinsic amidolytic or plasminogen activator activities.Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 11;30(23):5797-805. doi: 10.1021/bi00237a024. Biochemistry. 1991. PMID: 1828371
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and its receptor (CD87): a new target in tumor invasion and metastasis.J Obstet Gynaecol (Tokyo 1995). 1995 Apr;21(2):151-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.1995.tb01089.x. J Obstet Gynaecol (Tokyo 1995). 1995. PMID: 8556577 Review.
-
Interference with the urokinase plasminogen activator system: a promising therapy concept for solid tumours.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2001 Jul;1(4):683-91. doi: 10.1517/14712598.1.4.683. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2001. PMID: 11727504 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant-Derived Compounds and Extracts as Modulators of Plasmin Activity-A Review.Molecules. 2023 Feb 9;28(4):1677. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041677. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838662 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baldini E., Sorrenti S., D’Armiento E., di Matteo F.M., Catania A., Ulisse S. The urokinase plasminogen activating system in thyroid cancer: Clinical implications. G. Chir. 2012;33:305–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

