Missed opportunities for depression screening in patients with arthritis in the United States
- PMID: 23897128
- PMCID: PMC3832729
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-013-2541-y
Missed opportunities for depression screening in patients with arthritis in the United States
Abstract
Background: Arthritis affects 20 % of the adult US population and is associated with comorbid depression. Depression screening guidelines have been endorsed for high-risk groups, including persons with arthritis, in the hopes that screening will increase recognition and use of appropriate interventions.
Objective: To examine national rates of depression and depression screening for patients with arthritis between 2006 and 2010.
Participants and design: We used nationally representative cross-sections of ambulatory visits in the United States from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey from 2006 to 2010, which included 18,507 visits with a diagnosis of arthritis. When weighted to the US population, this total represents approximately 644 million visits.
Measurements: Visits where arthritis was listed among diagnoses. Outcomes were survey-weighted estimates of depression and prevalence of depression screening among patients with arthritis across patient and physician characteristics.
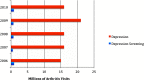
Key results: Of the 644,419,374 visits with arthritis listed, 83,574,127 (13 %) were associated with a comorbid diagnosis of depression. The odds ratio for comorbid depression with arthritis was 1.42 (95 % CI 1.3, 1.5). Depression screening occurred at 3,835,000 (1 %) visits associated with arthritis. When examining the rates of depression screening between ambulatory visits with and without arthritis listed, there was no difference in depression screening rates; both were approximately 1 %. There was no difference in screening rates by provider type. Compared to visits with other common, chronic conditions, the prevalence of depression at arthritis visits was high (13 per 100 visits), although the prevalence of depression screening at arthritis visits was low (0.68 per 100 visits).
Conclusions: Despite the high prevalence of depression with arthritis, screening for depression was performed at few arthritis visits, representing missed opportunities to detect a common, serious comorbidity. Improved depression screening by providers would identify affected patients, and may lead to appropriate interventions such as mental health referrals and/or treatment with anti-depressants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Screening in Depression Diagnosis and Treatment in a Representative Sample of US Primary Care Visits.J Gen Intern Med. 2020 Jan;35(1):12-20. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-05192-3. Epub 2019 Aug 6. J Gen Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 31388917 Free PMC article.
-
Depression prevalence, screening, and treatment in adult outpatients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: A nationally representative cross-sectional study (National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey 2014-2019).J Affect Disord. 2025 Jan 1;368:471-476. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.09.088. Epub 2024 Sep 16. J Affect Disord. 2025. PMID: 39293603
-
National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2001 summary.Adv Data. 2003 Aug 11;(337):1-44. Adv Data. 2003. PMID: 12924075
-
Effects of the 2009 USPSTF Depression Screening Recommendation on Diagnosing and Treating Mental Health Conditions in Older Adults: A Difference-in-Differences Analysis.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018 Aug;24(8):769-776. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2018.24.8.769. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30058984 Free PMC article.
-
Ambulatory care visits to physician offices, hospital outpatient departments, and emergency departments: United States, 1997.Vital Health Stat 13. 1999 Nov;(143):i-iv, 1-39. Vital Health Stat 13. 1999. PMID: 10633576 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis of Mental Disorders Complicated by Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Study of the Validity of a Questionnaire Method and Diagnosis by the Psychiatrist.Eur J Rheumatol. 2024 Nov 28;11(4):405-409. doi: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2024.24014. Eur J Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39651874 Free PMC article.
-
Is the serum oxytocin level altered by treatment in rheumatoid arthritis patients complicated with depression?Eur J Rheumatol. 2018 Mar;5(1):22-26. doi: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2018.17021. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Eur J Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29657870 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for depression with the PHQ-9 in young adults affected by HIV.J Affect Disord. 2022 Jan 15;297:276-282. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.10.037. Epub 2021 Oct 22. J Affect Disord. 2022. PMID: 34695500 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of alcohol consumption and mental health with the prevalence of arthritis among US adults: data from the 2012 National Health Interview Survey.Rheumatol Int. 2014 Sep;34(9):1241-9. doi: 10.1007/s00296-014-2992-4. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Rheumatol Int. 2014. PMID: 24667977
-
The Relationship between the Serum Oxytocin Levels, Disease Activity, the ADLs and the QOL in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Intern Med. 2017 Dec 1;56(23):3167-3172. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9191-17. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 29021442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sale JE, Gignac M, Hawker G. The relationship between disease symptoms, life events, coping and treatment, and depression among older adults with osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(2):335–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical