Analysis of periplasmic sensor domains from Anaeromyxobacter dehalogenans 2CP-C: structure of one sensor domain from a histidine kinase and another from a chemotaxis protein
- PMID: 23897711
- PMCID: PMC3831638
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.112
Analysis of periplasmic sensor domains from Anaeromyxobacter dehalogenans 2CP-C: structure of one sensor domain from a histidine kinase and another from a chemotaxis protein
Abstract
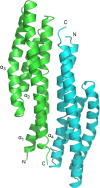
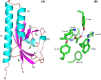
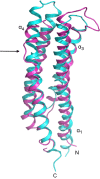
Anaeromyxobacter dehalogenans is a δ-proteobacterium found in diverse soils and sediments. It is of interest in bioremediation efforts due to its dechlorination and metal-reducing capabilities. To gain an understanding on A. dehalogenans' abilities to adapt to diverse environments we analyzed its signal transduction proteins. The A. dehalogenans genome codes for a large number of sensor histidine kinases (HK) and methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins (MCP); among these 23 HK and 11 MCP proteins have a sensor domain in the periplasm. These proteins most likely contribute to adaptation to the organism's surroundings. We predicted their three-dimensional folds and determined the structures of two of the periplasmic sensor domains by X-ray diffraction. Most of the domains are predicted to have either PAS-like or helical bundle structures, with two predicted to have solute-binding protein fold, and another predicted to have a 6-phosphogluconolactonase like fold. Atomic structures of two sensor domains confirmed the respective fold predictions. The Adeh_2942 sensor (HK) was found to have a helical bundle structure, and the Adeh_3718 sensor (MCP) has a PAS-like structure. Interestingly, the Adeh_3718 sensor has an acetate moiety bound in a binding site typical for PAS-like domains. Future work is needed to determine whether Adeh_3718 is involved in acetate sensing by A. dehalogenans.
Keywords: Acetate; PAS-like; chemotaxis; helical bundle; periplasmic sensor domains; sensor histidine kinase.
© 2013 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phosphotransfer site of the chemotaxis-specific protein kinase CheA as revealed by NMR.Biochemistry. 1997 Jan 28;36(4):699-710. doi: 10.1021/bi961663p. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9020767
-
Structural characterization of the heme-based oxygen sensor, AfGcHK, its interactions with the cognate response regulator, and their combined mechanism of action in a bacterial two-component signaling system.Proteins. 2016 Oct;84(10):1375-89. doi: 10.1002/prot.25083. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Proteins. 2016. PMID: 27273553
-
The NMR structure of the sensory domain of the membranous two-component fumarate sensor (histidine protein kinase) DcuS of Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 3;278(40):39185-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C300344200. Epub 2003 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12907689
-
Phosphohistidines in bacterial signaling.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997 Dec;7(6):793-7. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(97)80148-0. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997. PMID: 9434897 Review.
-
Signal transduction: hair brains in bacterial chemotaxis.Curr Biol. 2000 Jan 13;10(1):R11-4. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)00248-1. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10660286 Review.
Cited by
-
Sinorhizobium meliloti Chemoreceptor McpV Senses Short-Chain Carboxylates via Direct Binding.J Bacteriol. 2018 Nov 6;200(23):e00519-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00519-18. Print 2018 Dec 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 30201781 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic Analysis with Prediction of Cofactor or Ligand Binding for Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAS and Cache Domains.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0102621. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01026-21. Epub 2021 Dec 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34937179 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Mechanism of Nitrate Chemotaxis via Direct Ligand Binding to the PilJ Domain of McpN.mBio. 2019 Feb 19;10(1):e02334-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02334-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30782655 Free PMC article.
-
Control of phosphodiesterase activity in the regulator of biofilm dispersal RbdA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.RSC Chem Biol. 2024 Aug 27;5(10):1052-9. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00113c. Online ahead of print. RSC Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39247681 Free PMC article.
-
Assorted dysfunctions of endosomal alkali cation/proton exchanger SLC9A6 variants linked to Christianson syndrome.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 15;295(20):7075-7095. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.012614. Epub 2020 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32277048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anantharaman V, Arvind L. Cache – a signaling domain common to Ca2+- channel subunits and a class of prokaryotic chemotaxis receptors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000;25:535–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

