Metastasis suppressor tetraspanin CD82/KAI1 regulates ubiquitylation of epidermal growth factor receptor
- PMID: 23897813
- PMCID: PMC3764837
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.439380
Metastasis suppressor tetraspanin CD82/KAI1 regulates ubiquitylation of epidermal growth factor receptor
Abstract
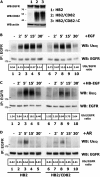
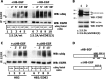
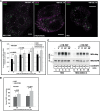
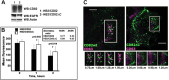
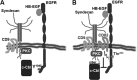
Ligand-induced ubiquitylation of EGF receptor (EGFR) is an important regulatory mechanism that controls endocytic trafficking of the receptor and its signaling potential. Here we report that tetraspanin CD82/KAI1 specifically suppresses ubiquitylation of EGFR after stimulation with heparin-binding EGF or amphiregulin and alters the rate of recruitment of the activated receptor to EEA1-positive endosomes. The suppressive effect of CD82 is dependent on the heparin-binding domain of the ligand. Deletion of the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of CD82 (CD82ΔC mutant) inhibits endocytic trafficking of the tetraspanin and compromises its activity toward heparin-binding EGF-activated EGFR. Reduced ubiquitylation of EGFR is accompanied by PKC-dependent increase in serine phosphorylation of c-Cbl in cells expressing elevated levels of CD82. Furthermore, phosphorylation of threonine 654 (PKC phosphorylation site) in the juxtamembrane domain of the receptor is considerably increased in CD82-expressing cells. These results describe previously unsuspected links between tetraspanin proteins and ubiquitylation of their molecular partners (e.g., EGFR). Our data identify CD82 as a new regulator of c-Cbl, which discriminatively controls the activity of this E3 ubiquitin ligase toward heparin-binding ligand-EGFR pairs. Taken together, these observations provide an important new insight into the modulatory role of CD82 in endocytic trafficking of EGF receptor.
Keywords: CD82; Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR); Heparin-binding Protein; Tetraspanins; Trafficking; Ubiquitylation.
Figures
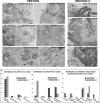
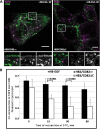
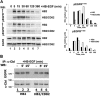
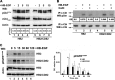
References
-
- Berditchevski F. (2001) Complexes of tetraspanins with integrins. More than meets the eye. J. Cell Sci. 114, 4143–4151 - PubMed
-
- Hemler M. (2003) Tetraspanin proteins mediate cellular penetration, invasion, and fusion events and define a novel type of membrane microdomain. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 19, 397–422 - PubMed
-
- Charrin S., le Naour F., Silvie O., Milhiet P.-E., Boucheix C., Rubinstein E. (2009) Lateral organisation of membrane proteins. tetraspanins spin their web. Biochem. J. 420, 133–154 - PubMed
-
- Berditchevski F., Odintsova E. (2007) Tetraspanins as regulators of protein trafficking. Traffic 8, 89–96 - PubMed
-
- Odintsova E., Sugiura T., Berditchevski F. (2000) Attenuation of EGF receptor signaling by a metastasis suppressor, the tetraspanin CD82/KAI-1. Curr. Biol. 10, 1009–1012 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

