Glia maturation factor (GMF) interacts with Arp2/3 complex in a nucleotide state-dependent manner
- PMID: 23897816
- PMCID: PMC3764776
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C113.493338
Glia maturation factor (GMF) interacts with Arp2/3 complex in a nucleotide state-dependent manner
Abstract
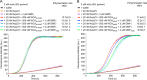
Glia maturation factor (GMF) is a member of the actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF)/cofilin family. ADF/cofilin promotes disassembly of aged actin filaments, whereas GMF interacts specifically with Arp2/3 complex at branch junctions and promotes debranching. A distinguishing feature of ADF/cofilin is that it binds tighter to ADP-bound than to ATP-bound monomeric or filamentous actin. The interaction is also regulated by phosphorylation at Ser-3 of mammalian cofilin, which inhibits binding to actin. However, it is unknown whether these two factors play a role in the interaction of GMF with Arp2/3 complex. Here we show using isothermal titration calorimetry that mammalian GMF has very low affinity for ATP-bound Arp2/3 complex but binds ADP-bound Arp2/3 complex with 0.7 μM affinity. The phosphomimetic mutation S2E in GMF inhibits this interaction. GMF does not bind monomeric ATP- or ADP-actin, confirming its specificity for Arp2/3 complex. We further show that mammalian Arp2/3 complex nucleation activated by the WCA region of the nucleation-promoting factor N-WASP is not affected by GMF, whereas nucleation activated by the WCA region of WAVE2 is slightly inhibited at high GMF concentrations. Together, the results suggest that GMF functions by a mechanism similar to that of other ADF/cofilin family members, displaying a preference for ADP-Arp2/3 complex and undergoing inhibition by phosphorylation of a serine residue near the N terminus. Arp2/3 complex nucleation occurs in the ATP state, and nucleotide hydrolysis promotes debranching, suggesting that the higher affinity of GMF for ADP-Arp2/3 complex plays a physiological role by promoting debranching of aged branch junctions without interfering with Arp2/3 complex nucleation.
Keywords: ADP; ATP; Actin; Arp2/3 Complex; GMF; Isothermal Titration Calorimetry; Protein Phosphorylation.
Figures

References
-
- Poukkula M., Kremneva E., Serlachius M., Lappalainen P. (2011) Actin-depolymerizing factor homology domain: a conserved fold performing diverse roles in cytoskeletal dynamics. Cytoskeleton 68, 471–490 - PubMed
-
- Inagaki M., Aoyama M., Sobue K., Yamamoto N., Morishima T., Moriyama A., Katsuya H., Asai K. (2004) Sensitive immunoassays for human and rat GMFB and GMFG, tissue distribution and age-related changes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1670, 208–216 - PubMed
-
- Ikeda K., Kundu R. K., Ikeda S., Kobara M., Matsubara H., Quertermous T. (2006) Glia maturation factor-γ is preferentially expressed in microvascular endothelial and inflammatory cells and modulates actin cytoskeleton reorganization. Circ. Res. 99, 424–433 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

