Alteration of endoplasmic reticulum lipid rafts contributes to lipotoxicity in pancreatic β-cells
- PMID: 23897822
- PMCID: PMC3772204
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.489310
Alteration of endoplasmic reticulum lipid rafts contributes to lipotoxicity in pancreatic β-cells
Abstract
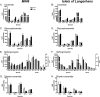
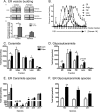
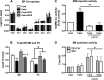
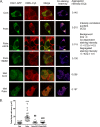
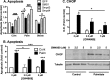
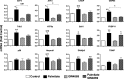
Chronic saturated fatty acid exposure causes β-cell apoptosis and, thus, contributes to type 2 diabetes. Although endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and reduced ER-to-Golgi protein trafficking have been implicated, the exact mechanisms whereby saturated fatty acids trigger β-cell death remain elusive. Using mass spectroscopic lipidomics and subcellular fractionation, we demonstrate that palmitate pretreatment of MIN6 β-cells promoted ER remodeling of both phospholipids and sphingolipids, but only the latter was causally linked to lipotoxic ER stress. Thus, overexpression of glucosylceramide synthase, previously shown to protect against defective protein trafficking and ER stress, partially reversed lipotoxic reductions in ER sphingomyelin (SM) content and aggregation of ER lipid rafts, as visualized using Erlin1-GFP. Using both lipidomics and a sterol response element reporter assay, we confirmed that free cholesterol in the ER was also reciprocally modulated by chronic palmitate and glucosylceramide synthase overexpression. This is consistent with the known coregulation and association of SM and free cholesterol in lipid rafts. Inhibition of SM hydrolysis partially protected against ATF4/C/EBP homology protein induction because of palmitate. Our results suggest that loss of SM in the ER is a key event for initiating β-cell lipotoxicity, which leads to disruption of ER lipid rafts, perturbation of protein trafficking, and initiation of ER stress.
Keywords: Ceramide; ER Lipid Raft; Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress; Lipidomics; Lipotoxicity; Palmitate; Pancreatic Islets; Sphingomyelin; Trafficking; Type 2 Diabetes.
Figures
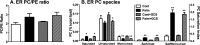
References
-
- Paolisso G., Tataranni P. A., Foley J. E., Bogardus C., Howard B. V., Ravussin E. (1995) A high concentration of fasting plasma non-esterified fatty acids is a risk factor for the development of NIDDM. Diabetologia 38, 1213–1217 - PubMed
-
- Kahn S. E., Hull R. L., Utzschneider K. M. (2006) Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 444, 840–846 - PubMed
-
- Weir G. C., Bonner-Weir S. (2004) Five stages of evolving β-cell dysfunction during progression to diabetes. Diabetes 53, S16–21 - PubMed
-
- Shimabukuro M., Higa M., Zhou Y. T., Wang M. Y., Newgard C. B., Unger R. H. (1998) Lipoapoptosis in β-cells of obese prediabetic fa/fa rats. Role of serine palmitoyltransferase overexpression. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 32487–32490 - PubMed
-
- El-Assaad W., Joly E., Barbeau A., Sladek R., Buteau J., Maestre I., Pepin E., Zhao S., Iglesias J., Roche E., Prentki M. (2010) Glucolipotoxicity alters lipid partitioning and causes mitochondrial dysfunction, cholesterol, and ceramide deposition and reactive oxygen species production in INS832/13 ss-cells. Endocrinology 151, 3061–3073 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

