Submergence confers immunity mediated by the WRKY22 transcription factor in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 23897923
- PMCID: PMC3753392
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.113.114447
Submergence confers immunity mediated by the WRKY22 transcription factor in Arabidopsis
Abstract
Transcriptional control plays an important role in regulating submergence responses in plants. Although numerous genes are highly induced during hypoxia, their individual roles in hypoxic responses are still poorly understood. Here, we found that expression of genes that encode members of the WRKY transcription factor family was rapidly and strongly induced upon submergence in Arabidopsis thaliana, and this induction correlated with induction of a large portion of innate immunity marker genes. Furthermore, prior submergence treatment conferred higher resistance to the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae in Arabidopsis. Among the WRKY genes tested, WRKY22 had the highest level of induction during the early stages of submergence. Compared with the wild type, WRKY22 T-DNA insertion mutants wrky22-1 and wrky22-2 had lower disease resistance and lower induction of innate immunity markers, such as FLG22-INDUCED RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE1 (FRK1) and WRKY53, after submergence. Furthermore, transcriptomic analyses of wrky22-2 and chromatin immunoprecipitation identified several potential targets of WRKY22, which included genes encoding a TIR domain-containing protein, a plant peptide hormone, and many OLIGO PEPTIDE TRANSPORTER genes, all of which may lead to induction of innate immunity. In conclusion, we propose that submergence triggers innate immunity in Arabidopsis via WRKY22, a response that may protect against a higher probability of pathogen infection either during or after flooding.
Figures
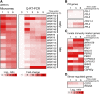




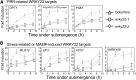
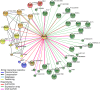

Similar articles
-
STRESS INDUCED FACTOR 2, a Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase Regulates Basal Plant Pathogen Defense.Plant Physiol. 2018 Apr;176(4):3062-3080. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01266. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29463771 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis WRKY46 coordinates with WRKY70 and WRKY53 in basal resistance against pathogen Pseudomonas syringae.Plant Sci. 2012 Apr;185-186:288-97. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.12.003. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22325892
-
Arabidopsis cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase 45 positively regulates disease resistance to Pseudomonas syringae.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2013 Dec;73:383-91. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.10.024. Epub 2013 Oct 26. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 24215930
-
Transcription Factors as the "Blitzkrieg" of Plant Defense: A Pragmatic View of Nitric Oxide's Role in Gene Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 7;22(2):522. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020522. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33430258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabidopsis at 7: still growing like a weed.Plant Cell. 1996 Nov;8(11):1917-33. doi: 10.1105/tpc.8.11.1917. Plant Cell. 1996. PMID: 8953765 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
WRKY Transcription Factors: Molecular Regulation and Stress Responses in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Jun 3;7:760. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00760. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27375634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights into the Connections between Flooding/Hypoxia Response and Plant Defenses against Pathogens.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 6;13(16):2176. doi: 10.3390/plants13162176. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomics of temperature-sensitive R gene-mediated resistance identifies a WAKL10 protein interaction network.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 29;14(1):5023. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53643-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38424101 Free PMC article.
-
Time-Course Transcriptomics Analysis Reveals Key Responses of Submerged Deepwater Rice to Flooding.Plant Physiol. 2018 Apr;176(4):3081-3102. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00858. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29475897 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis acyl-CoA-binding protein ACBP3 participates in plant response to hypoxia by modulating very-long-chain fatty acid metabolism.Plant J. 2015 Jan;81(1):53-67. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12692. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Plant J. 2015. PMID: 25284079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asai T., Tena G., Plotnikova J., Willmann M.R., Chiu W.-L., Gomez-Gomez L., Boller T., Ausubel F.M., Sheen J. (2002). MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415: 977–983 - PubMed
-
- Bailey-Serres J., Voesenek L.A.C.J. (2008). Flooding stress: Acclimations and genetic diversity. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 59: 313–339 - PubMed
-
- Bieniawska Z., Paul Barratt D.H., Garlick A.P., Thole V., Kruger N.J., Martin C., Zrenner R., Smith A.M. (2007). Analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 49: 810–828 - PubMed
-
- Boller T., Felix G. (2009). A renaissance of elicitors: Perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 60: 379–406 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

