Rates and outcomes of follicular lymphoma transformation in the immunochemotherapy era: a report from the University of Iowa/MayoClinic Specialized Program of Research Excellence Molecular Epidemiology Resource
- PMID: 23897955
- PMCID: PMC3757293
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2012.48.3990
Rates and outcomes of follicular lymphoma transformation in the immunochemotherapy era: a report from the University of Iowa/MayoClinic Specialized Program of Research Excellence Molecular Epidemiology Resource
Abstract
Purpose: This study sought to characterize transformation incidence and outcome for patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) in a prospective observational series begun after diffusion of rituximab use.
Patients and methods: Patients with newly diagnosed FL were prospectively enrolled onto the University of Iowa/Mayo Clinic Specialized Program of Research Excellence Molecular Epidemiology Resource from 2002 to 2009. Patients were actively followed for re-treatment, clinical or pathologic transformation, and death. Risk of transformation was analyzed via time to transformation by using death as a competing risk.
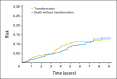
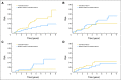
Results: In all, there were 631 patients with newly diagnosed grade 1 to 3a FL who had a median age at enrollment of 60 years. At a median follow-up of 60 months (range, 11 to 110 months), 79 patients had died, and 60 patients developed transformed lymphoma, of which 51 were biopsy proven. The overall transformation rate at 5 years was 10.7%, with an estimated rate of 2% per year. Increased lactate dehydrogenase was associated with increased risk of transformation. Transformation rate at 5 years was highest in patients who were initially observed and lowest in patients who initially received rituximab monotherapy (14.4% v 3.2%; P = .021). Median overall survival following transformation was 50 months and was superior in patients with transformation greater than 18 months after FL diagnosis compared with patients with earlier transformation (5-year overall survival, 66% v 22%; P < .001).
Conclusion: Follicular transformation rates in the immunochemotherapy era are similar to risk of death without transformation and may be lower than reported in older series. Post-transformation prognosis is substantially better than described in older series. Initial management strategies may influence the risk of transformation.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Herold M, Haas A, Srock S, et al. Rituximab added to first-line mitoxantrone, chlorambucil, and prednisolone chemotherapy followed by interferon maintenance prolongs survival in patients with advanced follicular lymphoma: An East German Study Group Hematology and Oncology Study. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1986–1992. - PubMed
-
- Hiddemann W, Kneba M, Dreyling M, et al. Frontline therapy with rituximab added to the combination of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) significantly improves the outcome for patients with advanced-stage follicular lymphoma compared with therapy with CHOP alone: Results of a prospective randomized study of the German Low-Grade Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 2005;106:3725–3732. - PubMed
-
- Marcus R, Imrie K, Belch A, et al. CVP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CVP as first-line treatment for advanced follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2005;105:1417–1423. - PubMed
-
- Salles G, Mounier N, de Guibert S, et al. Rituximab combined with chemotherapy and interferon in follicular lymphoma patients: Results of the GELA-GOELAMS FL2000 study. Blood. 2008;112:4824–4831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

