Bulbar and speech motor assessment in ALS: challenges and future directions
- PMID: 23898888
- PMCID: PMC3833808
- DOI: 10.3109/21678421.2013.817585
Bulbar and speech motor assessment in ALS: challenges and future directions
Abstract
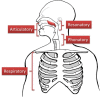
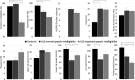
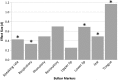
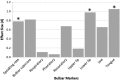
Bulbar motor deterioration due to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) leads to the eventual impairment of speech and swallowing functions. Despite these devastating consequences, no standardized diagnostic procedure for assessing bulbar dysfunction in ALS exists and adequate objective markers of bulbar deterioration have not been identified. In this paper, we consider objective measures of speech motor function, which show promise for forming the basis of a comprehensive, quantitative bulbar motor assessment in ALS. These measures are based on the assessment of four speech subsystems: respiratory, phonatory, articulatory, and resonatory. The goal of this research is to design a non-invasive, comprehensive bulbar motor assessment instrument intended for early detection, monitoring of disease progression, and clinical trial application. Preliminary data from an ongoing study of bulbar motor decline are presented, which demonstrate the potential clinical efficacy of the speech subsystem approach.
Figures
References
-
- Haverkamp LJ, Appel V, Appel SH. Natural history of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a database population. Validation of a scoring system and a model for survival prediction. Brain. 1995;118:707–19. - PubMed
-
- Armon C, Moses D. Linear estimates of rates of disease progression as predictors of survival in patients with ALS entering clinical trials. J Neurol Sci. 1998;160:37–41. - PubMed
-
- del Aguila MA, Longstreth WT, Jr, McGuire V, Koepsell TD, van Belle G. Prognosis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a population based study. Neurology. 2003;60:813–9. - PubMed
-
- Ball L, Beukelman DR, Pattee G. Timing of speech deterioration in people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Med Speech-Lang Pa. 2002;10:231–5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
