11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: intracellular gate-keepers of tissue glucocorticoid action
- PMID: 23899562
- PMCID: PMC3962546
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00020.2012
11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: intracellular gate-keepers of tissue glucocorticoid action
Abstract
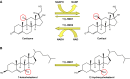
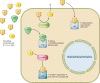
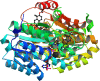
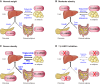
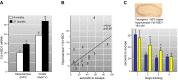
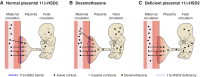
Glucocorticoid action on target tissues is determined by the density of "nuclear" receptors and intracellular metabolism by the two isozymes of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (11β-HSD) which catalyze interconversion of active cortisol and corticosterone with inert cortisone and 11-dehydrocorticosterone. 11β-HSD type 1, a predominant reductase in most intact cells, catalyzes the regeneration of active glucocorticoids, thus amplifying cellular action. 11β-HSD1 is widely expressed in liver, adipose tissue, muscle, pancreatic islets, adult brain, inflammatory cells, and gonads. 11β-HSD1 is selectively elevated in adipose tissue in obesity where it contributes to metabolic complications. Similarly, 11β-HSD1 is elevated in the ageing brain where it exacerbates glucocorticoid-associated cognitive decline. Deficiency or selective inhibition of 11β-HSD1 improves multiple metabolic syndrome parameters in rodent models and human clinical trials and similarly improves cognitive function with ageing. The efficacy of inhibitors in human therapy remains unclear. 11β-HSD2 is a high-affinity dehydrogenase that inactivates glucocorticoids. In the distal nephron, 11β-HSD2 ensures that only aldosterone is an agonist at mineralocorticoid receptors (MR). 11β-HSD2 inhibition or genetic deficiency causes apparent mineralocorticoid excess and hypertension due to inappropriate glucocorticoid activation of renal MR. The placenta and fetus also highly express 11β-HSD2 which, by inactivating glucocorticoids, prevents premature maturation of fetal tissues and consequent developmental "programming." The role of 11β-HSD2 as a marker of programming is being explored. The 11β-HSDs thus illuminate the emerging biology of intracrine control, afford important insights into human pathogenesis, and offer new tissue-restricted therapeutic avenues.
Figures



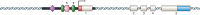


References
-
- Abdallah BM, Beck-Nielsen H, Gaster M. Increased expression of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in type 2 diabetic myotubes. Eur J Clin Invest 35: 627–634, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Ackermann D, Vogt B, Escher G, Dick B, Reichen J, Frey BM, Frey FJ. Inhibition of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase by bile acids in rats with cirrhosis. Hepatology 30: 623–629, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Agarwal AK, Giacchetti G, Lavery G, Nikkila H, Palermo M, Ricketts M, McTernan C, Bianchi G, Manunta P, Strazzullo P, Mantero F, White PC, Stewart PM. CA-repeat polymorphism in intron 1 of HSD11B2: effects on gene expression and salt sensitivity. Hypertension 36: 187–194, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Agarwal AK, Monder C, Eckstein B, White PC. Cloning and expression of rat cDNA encoding corticosteroid 11 beta-dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 264: 18939–18943, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Agarwal AK, Mune T, Monder C, White PC. Mutations in putative glycosylation sites of rat 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase affect enzymatic-activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1248: 70–74, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

