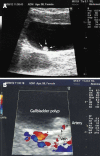
Gallbladder polyps: factors affecting surgical decision
- PMID: 23901228
- PMCID: PMC3725377
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4526
Gallbladder polyps: factors affecting surgical decision
Abstract
Aim: To determine the factors affecting the decision to perform surgery, and the efficiency of ultrasonography (USG) in detecting gallbladder polyps (GP).
Methods: Data for 138 patients who underwent cholecystectomy between 1996 and 2012 in our clinic with a diagnosis of GP were retrospectively analyzed. Demographic data, clinical presentation, principal symptoms, ultrasonographic and histopathological findings were evaluated. Patients were evaluated in individual groups according to the age of the patients (older or younger than 50 years old) and polyp size (bigger or smaller than 10 mm) and characteristics of the polyps (pseudopolyp or real polyps). χ(2) tests were used for the statistical evaluation of the data.
Results: The median age was 50 (26-85) years and 91 of patients were female. Of 138 patients who underwent cholecystectomy with GP diagnosis, only 99 had a histopathologically defined polyp; 77 of them had pseudopolyps and 22 had true polyps. Twenty-one patients had adenocarcinoma. Of these 21 patients, 11 were male, their median age was 61 (40-85) years and all malignant polyps had diameters > 10 mm (P < 0.0001). Of 138 patients in whom surgery were performed, 112 had ultrasonographic polyps with diameters < 10 mm. Of the other 26 patients who also had polyps with diameters > 10 mm, 22 had true polyps. The sensitivity of USG was 84.6% for polyps with diameters > 10 mm (P < 0.0001); however it was only 66% in polyps with diameters < 10 mm.
Conclusion: The risk of malignancy was high in the patients over 50 years old who had single polyps with diameters > 10 mm.
Keywords: Cholecystectomy; Gallbladder; Malignancy; Polyps; Ultrasound.
Figures
References
-
- Zielinski MD, Atwell TD, Davis PW, Kendrick ML, Que FG. Comparison of surgically resected polypoid lesions of the gallbladder to their pre-operative ultrasound characteristics. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009;13:19–25. - PubMed
-
- Lee KF, Wong J, Li JC, Lai PB. Polypoid lesions of the gallbladder. Am J Surg. 2004;188:186–190. - PubMed
-
- Terzi C, Sökmen S, Seçkin S, Albayrak L, Uğurlu M. Polypoid lesions of the gallbladder: report of 100 cases with special reference to operative indications. Surgery. 2000;127:622–627. - PubMed
-
- Yang HL, Sun YG, Wang Z. Polypoid lesions of the gallbladder: diagnosis and indications for surgery. Br J Surg. 1992;79:227–229. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical