True progression versus pseudoprogression in the treatment of glioblastomas: a comparison study of normalized cerebral blood volume and apparent diffusion coefficient by histogram analysis
- PMID: 23901325
- PMCID: PMC3725362
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.4.662
True progression versus pseudoprogression in the treatment of glioblastomas: a comparison study of normalized cerebral blood volume and apparent diffusion coefficient by histogram analysis
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to differentiate true progression from pseudoprogression of glioblastomas treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) with temozolomide (TMZ) by using histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and normalized cerebral blood volume (nCBV) maps.
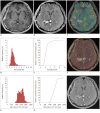
Materials and methods: Twenty patients with histopathologically proven glioblastoma who had received CCRT with TMZ underwent perfusion-weighted imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging (b = 0, 1000 sec/mm(2)). The corresponding nCBV and ADC maps for the newly visible, entirely enhancing lesions were calculated after the completion of CCRT with TMZ. Two observers independently measured the histogram parameters of the nCBV and ADC maps. The histogram parameters between the true progression group (n = 10) and the pseudoprogression group (n = 10) were compared by use of an unpaired Student's t test and subsequent multivariable stepwise logistic regression analysis to determine the best predictors for the differential diagnosis between the two groups. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was employed to determine the best cutoff values for the histogram parameters that proved to be significant predictors for differentiating true progression from pseudoprogression. Intraclass correlation coefficient was used to determine the level of inter-observer reliability for the histogram parameters.
Results: The 5th percentile value (C5) of the cumulative ADC histograms was a significant predictor for the differential diagnosis between true progression and pseudoprogression (p = 0.044 for observer 1; p = 0.011 for observer 2). Optimal cutoff values of 892 × 10(-6) mm(2)/sec for observer 1 and 907 × 10(-6) mm(2)/sec for observer 2 could help differentiate between the two groups with a sensitivity of 90% and 80%, respectively, a specificity of 90% and 80%, respectively, and an area under the curve of 0.880 and 0.840, respectively. There was no other significant differentiating parameter on the nCBV histograms. Inter-observer reliability was excellent or good for all histogram parameters (intraclass correlation coefficient range: 0.70-0.99).
Conclusion: The C5 of the cumulative ADC histogram can be a promising parameter for the differentiation of true progression from pseudoprogression of newly visible, entirely enhancing lesions after CCRT with TMZ for glioblastomas.
Keywords: Apparent diffusion coefficient; Cerebral blood volume; Glioblastoma multiforme; Histogram analysis; Pseudoprogression.
Figures


References
-
- Jeon HJ, Kong DS, Park KB, Lee JI, Park K, Kim JH, et al. Clinical outcome of concomitant chemoradiotherapy followed by adjuvant temozolomide therapy for glioblastaomas: single-center experience. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009;111:679–682. - PubMed
-
- Erpolat OP, Akmansu M, Goksel F, Bora H, Yaman E, Büyükberber S. Outcome of newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients treated by radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide: a long-term analysis. Tumori. 2009;95:191–197. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC, Jr, Cairncross JG. Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8:1277–1280. - PubMed
-
- Taal W, Brandsma D, de Bruin HG, Bromberg JE, Swaak-Kragten AT, Smitt PA, et al. Incidence of early pseudo-progression in a cohort of malignant glioma patients treated with chemoirradiation with temozolomide. Cancer. 2008;113:405–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

