Class D β-lactamases: a reappraisal after five decades
- PMID: 23902256
- PMCID: PMC4018812
- DOI: 10.1021/ar300327a
Class D β-lactamases: a reappraisal after five decades
Abstract
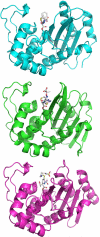
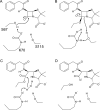
Despite 70 years of clinical use, β-lactam antibiotics still remain at the forefront of antimicrobial chemotherapy. The major challenge to these life-saving therapeutics is the presence of bacterial enzymes (i.e., β-lactamases) that can hydrolyze the β-lactam bond and inactivate the antibiotic. These enzymes can be grouped into four classes (A-D). Among the most genetically diverse are the class D β-lactamases. In this class are β-lactamases that can inactivate the entire spectrum of β-lactam antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems). Class D β-lactamases are mostly found in Gram-negative bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa , Escherichia coli , Proteus mirabilis , and Acinetobacter baumannii . The active-sites of class D β-lactamases contain an unusual N-carboxylated lysine post-translational modification. A strongly hydrophobic active-site helps create the conditions that allow the lysine to combine with CO2, and the resulting carbamate is stabilized by a number of hydrogen bonds. The carboxy-lysine plays a symmetric role in the reaction, serving as a general base to activate the serine nucleophile in the acylation reaction, and the deacylating water in the second step. There are more than 250 class D β-lactamases described, and the full set of variants shows remarkable diversity with regard to substrate binding and turnover. Narrow-spectrum variants are most effective against the earliest generation penicillins and cephalosporins such as ampicillin and cephalothin. Extended-spectrum variants (also known as extended-spectrum β-lactamases, ESBLs) pose a more dangerous clinical threat as they possess a small number of substitutions that allow them to bind and hydrolyze later generation cephalosporins that contain bulkier side-chain constituents (e.g., cefotaxime, ceftazidime, and cefepime). Mutations that permit this versatility seem to cluster in the area surrounding an active-site tryptophan resulting in a widened active-site to accommodate the oxyimino side-chains of these cephalosporins. More concerning are the class D β-lactamases that hydrolyze clinically important carbapenem β-lactam drugs (e.g., imipenem). Whereas carbapenems irreversibly acylate and inhibit narrow-spectrum β-lactamases, class D carbapenemases are able to recruit and activate a deacylating water. The rotational orientation of the C6 hydroxyethyl group found on all carbapenem antibiotics likely plays a role in whether the deacylating water is effective or not. Inhibition of class D β-lactamases is a current challenge. Commercially available inhibitors that are active against other classes of β-lactamases are ineffective against class D enzymes. On the horizon are several compounds, consisting of both β-lactam derivatives and non-β-lactams, that have the potential of providing novel leads to design new mechanism-based inactivators that are effective against the class D enzymes. Several act synergistically when given in combination with a β-lactam antibiotic, and others show a unique mechanism of inhibition that is distinct from the traditional β-lactamase inhibitors. These studies will bolster structure-based inhibitor design efforts to facilitate the optimization and development of these compounds as class D inactivators.
Figures

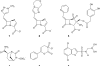
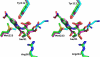
References
-
- McDermott W, Rogers DE. Social ramifications of control of microbial disease. Johns Hopkins Med. J. 1982;151:302–12. - PubMed
-
- Hujer KM, Hujer AM, Hulten EA, Bajaksouzian S, Adams JM, Donskey CJ, Ecker DJ, Massire C, Eshoo MW, Sampath R, Thomson JM, Rather PN, Craft DW, Fishbain JT, Ewell AJ, Jacobs MR, Paterson DL, Bonomo RA. Analysis of antibiotic resistance genes in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter sp. isolates from military and civilian patients treated at the Walter Reed Army Medical Center. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006;50:4114–23. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poirel L, Potron A, Nordmann P. OXA-48-like carbapenemases: the phantom menace. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012;67:1597–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

