A comparative phenotypic and genomic analysis of C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N mouse strains
- PMID: 23902802
- PMCID: PMC4053787
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-7-r82
A comparative phenotypic and genomic analysis of C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N mouse strains
Abstract
Background: The mouse inbred line C57BL/6J is widely used in mouse genetics and its genome has been incorporated into many genetic reference populations. More recently large initiatives such as the International Knockout Mouse Consortium (IKMC) are using the C57BL/6N mouse strain to generate null alleles for all mouse genes. Hence both strains are now widely used in mouse genetics studies. Here we perform a comprehensive genomic and phenotypic analysis of the two strains to identify differences that may influence their underlying genetic mechanisms.
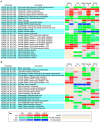
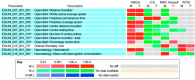
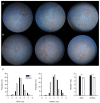
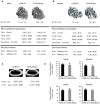
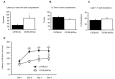
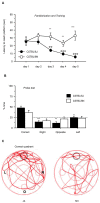
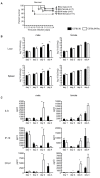
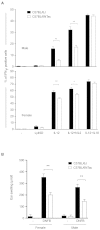
Results: We undertake genome sequence comparisons of C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N to identify SNPs, indels and structural variants, with a focus on identifying all coding variants. We annotate 34 SNPs and 2 indels that distinguish C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N coding sequences, as well as 15 structural variants that overlap a gene. In parallel we assess the comparative phenotypes of the two inbred lines utilizing the EMPReSSslim phenotyping pipeline, a broad based assessment encompassing diverse biological systems. We perform additional secondary phenotyping assessments to explore other phenotype domains and to elaborate phenotype differences identified in the primary assessment. We uncover significant phenotypic differences between the two lines, replicated across multiple centers, in a number of physiological, biochemical and behavioral systems.
Conclusions: Comparison of C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N demonstrates a range of phenotypic differences that have the potential to impact upon penetrance and expressivity of mutational effects in these strains. Moreover, the sequence variants we identify provide a set of candidate genes for the phenotypic differences observed between the two strains.
Figures
References
-
- Skarnes WC, Rosen B, West AP, Koutsourakis M, Bushell W, Iyer V, Mujica AO, Thomas M, Harrow J, Cox T, Jackson D, Severin J, Biggs P, Fu J, Nefedov M, de Jong PJ, Stewart AF, Bradley A. A conditional knockout resource for the genome-wide study of mouse gene function. Nature. 2011;14:337–342. doi: 10.1038/nature10163. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carneiro AM, Airey DC, Thompson B, Zhu CB, Lu L, Chesler EJ, Erikson KM, Blakely RD. Functional coding variation in recombinant inbred mouse lines reveals multiple serotonin transporter-associated phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;14:2047–2052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809449106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MC_U127561112/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0800024/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_1502/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0300212/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U142684175/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_QA137918/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561112/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U142684172/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 13031/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G1002082/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 100669/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_U142684171/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

