Autosomal dominant diabetes arising from a Wolfram syndrome 1 mutation
- PMID: 23903355
- PMCID: PMC3806620
- DOI: 10.2337/db13-0571
Autosomal dominant diabetes arising from a Wolfram syndrome 1 mutation
Abstract
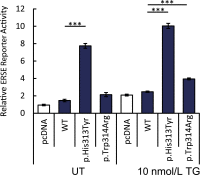
We used an unbiased genome-wide approach to identify exonic variants segregating with diabetes in a multigenerational Finnish family. At least eight members of this family presented with diabetes with age of diagnosis ranging from 18 to 51 years and a pattern suggesting autosomal dominant inheritance. We sequenced the exomes of four affected members of this family and performed follow-up genotyping of additional affected and unaffected family members. We uncovered a novel nonsynonymous variant (p.Trp314Arg) in the Wolfram syndrome 1 (WFS1) gene that segregates completely with the diabetic phenotype. Multipoint parametric linkage analysis with 13 members of this family identified a single linkage signal with maximum logarithm of odds score 3.01 at 4p16.2-p16.1, corresponding to a region harboring the WFS1 locus. Functional studies demonstrate a role for this variant in endoplasmic reticulum stress, which is consistent with the β-cell failure phenotype seen in mutation carriers. This represents the first compelling report of a mutation in WFS1 associated with dominantly inherited nonsyndromic adult-onset diabetes.
Figures




References
-
- Molven A, Njølstad PR. Role of molecular genetics in transforming diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 2011;11:313–320 - PubMed
-
- Steck AK, Winter WE. Review on monogenic diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2011;18:252–258 - PubMed
-
- Vaxillaire M, Bonnefond A, Froguel P. The lessons of early-onset monogenic diabetes for the understanding of diabetes pathogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;26:171–187 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK085501/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1ZIAHG000024/PHS HHS/United States
- DK-062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-TR-000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 1K99-DK-092251/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067493/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-016746/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK-020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK092251/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK016746/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085524/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA HG000024/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK092251/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085584/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK016746/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK-067493/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

