Complexity of receptor tyrosine kinase signal processing
- PMID: 23906711
- PMCID: PMC3721286
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009043
Complexity of receptor tyrosine kinase signal processing
Abstract
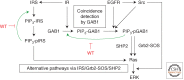
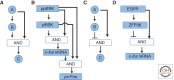
Our knowledge of molecular mechanisms of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling advances with ever-increasing pace. Yet our understanding of how the spatiotemporal dynamics of RTK signaling control specific cellular outcomes has lagged behind. Systems-centered experimental and computational approaches can help reveal how overlapping networks of signal transducers downstream of RTKs orchestrate specific cell-fate decisions. We discuss how RTK network regulatory structures, which involve the immediate posttranslational and delayed transcriptional controls by multiple feed forward and feedback loops together with pathway cross talk, adapt cells to the combinatorial variety of external cues and conditions. This intricate network circuitry endows cells with emerging capabilities for RTK signal processing and decoding. We illustrate how mathematical modeling facilitates our understanding of RTK network behaviors by unraveling specific systems properties, including bistability, oscillations, excitable responses, and generation of intricate landscapes of signaling activities.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modeling of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling: Computational and Experimental Protocols.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1636:417-453. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7154-1_27. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28730495
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases fall into distinct classes based on their inferred signaling networks.Sci Signal. 2013 Jul 16;6(284):ra58. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003994. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23861540 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Groucho mediates RTK feedback inhibition and prolonged pathway target gene expression.Curr Biol. 2011 Jul 12;21(13):1102-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.05.043. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21683597
-
Context-dependent regulation of receptor tyrosine kinases: Insights from systems biology approaches.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2019 Mar;11(2):e1437. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1437. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30255986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feedback regulation of RTK signaling in development.Dev Biol. 2019 Mar 1;447(1):71-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.10.017. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 29079424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases modulate distinct transcriptional programs by differential usage of intracellular pathways.Elife. 2015 May 7;4:e07186. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07186. Elife. 2015. PMID: 25951516 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Interplay between Expression, Mutation and Activity of ALK Receptor in Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells for Clinical Application of Small-Molecule Inhibitors.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0132330. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132330. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26147305 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Phosphatases and Kinases: How to Checkmate Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 28;9:690306. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.690306. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34778245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-function relationships of ErbB RTKs in the plasma membrane of living cells.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Apr 1;6(4):a008961. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008961. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 24691959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dynamic control of signal transduction networks in cancer cells.Nat Rev Cancer. 2015 Sep;15(9):515-27. doi: 10.1038/nrc3983. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26289315 Review.
References
-
- Aceto N, Sausgruber N, Brinkhaus H, Gaidatzis D, Martiny-Baron G, Mazzarol G, Confalonieri S, Quarto M, Hu G, Balwierz PJ, et al. 2012. Tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 promotes breast cancer progression and maintains tumor-initiating cells via activation of key transcription factors and a positive feedback signaling loop. Nat Med 18: 529–537 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad T, Farnie G, Bundred NJ, Anderson NG 2004. The mitogenic action of insulin-like growth factor I in normal human mammary epithelial cells requires the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 279: 1713–1719 - PubMed
-
- Amit I, Citri A, Shay T, Lu Y, Katz M, Zhang F, Tarcic G, Siwak D, Lahad J, Jacob-Hirsch J, et al. 2007. A module of negative feedback regulators defines growth factor signaling. Nat Genet 39: 503–512 - PubMed
-
- Avraham R, Yarden Y 2011. Feedback regulation of EGFR signalling: Decision making by early and delayed loops. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12: 104–117 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
