Titration of four replication factors is essential for the Xenopus laevis midblastula transition
- PMID: 23907533
- PMCID: PMC3898016
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1241530
Titration of four replication factors is essential for the Xenopus laevis midblastula transition
Abstract
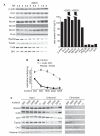
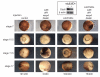
The rapid, reductive early divisions of many metazoan embryos are followed by the midblastula transition (MBT), during which the cell cycle elongates and zygotic transcription begins. It has been proposed that the increasing nuclear to cytoplasmic (N/C) ratio is critical for controlling the events of the MBT. We show that four DNA replication factors--Cut5, RecQ4, Treslin, and Drf1--are limiting for replication initiation at increasing N/C ratios in vitro and in vivo in Xenopus laevis. The levels of these factors regulate multiple events of the MBT, including the slowing of the cell cycle, the onset of zygotic transcription, and the developmental activation of the kinase Chk1. This work provides a mechanism for how the N/C ratio controls the MBT and shows that the regulation of replication initiation is fundamental for normal embryogenesis.
Figures


Comment in
-
Development: Replication factors make the transition.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 Sep;14(9):598. doi: 10.1038/nrg3562. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 23938364 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

