Autophagy in Myf5+ progenitors regulates energy and glucose homeostasis through control of brown fat and skeletal muscle development
- PMID: 23907538
- PMCID: PMC3790054
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2013.111
Autophagy in Myf5+ progenitors regulates energy and glucose homeostasis through control of brown fat and skeletal muscle development
Abstract
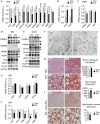
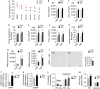
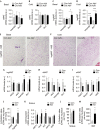
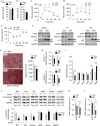
Macroautophagy (MA) regulates cellular quality control and energy balance. For example, loss of MA in aP2-positive adipocytes converts white adipose tissue (WAT) into brown adipose tissue (BAT)-like, enhancing BAT function and thereby insulin sensitivity. However, whether MA regulates early BAT development is unknown. We report that deleting Atg7 in myogenic Myf5+ progenitors inhibits MA in Myf5-cell-derived BAT and muscle. Knock out (KO) mice have defective BAT differentiation and function. Surprisingly, their body temperature is higher due to WAT lipolysis-driven increases in fatty acid oxidation in 'Beige' cells in inguinal WAT, BAT and muscle. KO mice also present impaired muscle differentiation, reduced muscle mass and glucose intolerance. Our studies show that ATG7 in Myf5+ progenitors is required to maintain energy and glucose homeostasis through effects on BAT and muscle development. Decreased MA in myogenic progenitors with age and/or overnutrition might contribute to the metabolic defects and sarcopenia observed in these conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K01 DK087776/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK033823/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK087776/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK033823/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK033823/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG043517/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007288/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG043517/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32GM728837/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK81412/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AG043517/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081412/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026687/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

