Lys63-linked polyubiquitination of BRAF at lysine 578 is required for BRAF-mediated signaling
- PMID: 23907581
- PMCID: PMC3731650
- DOI: 10.1038/srep02344
Lys63-linked polyubiquitination of BRAF at lysine 578 is required for BRAF-mediated signaling
Abstract
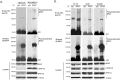
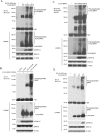
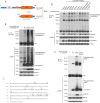
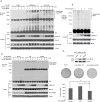
The RAF kinase family is essential in mediating signal transduction from RAS to ERK. BRAF constitutively active mutations correlate with human cancer development. However, the precise molecular regulation of BRAF activation is not fully understood. Here we report that BRAF is modified by Lys63-linked polyubiquitination at lysine 578 within its kinase domain once it is activated by gain of constitutively active mutation or epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulation. Substitution of BRAF lysine 578 with arginine (K578R) inhibited BRAF-mediated ERK activation. Furthermore, ectopic expression of BRAF K578R mutant inhibited anchorage-independent colony formation of MCF7 breast cancer cell line. Our studies have identified a previously unrecognized regulatory role of Lys63-linked polyubiquitination in BRAF-mediated normal and oncogenic signalings.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

