Is TKA using patient-specific instruments comparable to conventional TKA? A randomized controlled study of one system
- PMID: 23907610
- PMCID: PMC3825894
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-013-3206-1
Is TKA using patient-specific instruments comparable to conventional TKA? A randomized controlled study of one system
Abstract
Background: Patient-specific CT-based instrumentation may reduce implant malpositioning and improve alignment in TKA. However, it is not known whether this innovation is an advance that benefits patients.
Questions/purposes: We evaluated (1) the precision of patient-specific TKA by comparing the incidence of outliers in postoperative alignment between TKAs using patient-specific instruments and TKAs using conventional instruments, and (2) the reliability of patient-specific instruments by intraoperatively investigating whether the surgery could be completed with patient-specific instruments alone.
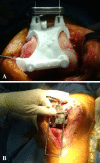
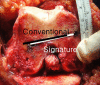
Methods: In this randomized controlled trial, we compared patient-specific TKA instruments from one manufacturer (n = 50) with conventional TKA instruments (n = 50). Postoperative hip-knee-ankle angles, femoral component rotation, and coronal and sagittal alignments of each component were measured. The validity of the patient-specific instrument was examined using cross-checking procedures with conventional instruments during the surgeries. When the procedure could not be completed accurately with patient-specific instruments, the procedure was converted to TKA using conventional instruments, and the frequency of this occurrence was tallied.
Results: Outliers in the hip-knee-ankle angle were comparable between groups (12% in the patient-specific instrument group and 10% in the conventional instrument group). Other parameters such as sagittal alignment and femoral component rotation did not differ in terms of outliers. Patient-specific guides were abandoned in eight knees (16%) during the surgery because of malrotation of the femoral components and decreased slope of the tibia.
Conclusions: Accuracy was comparable between TKAs done with patient-specific instruments and those done with conventional instruments. However, the patient-specific instrument procedures had to be aborted frequently, incurring expenses that did not benefit patients.
Figures
Comment in
-
CORR Insights ®: Is TKA using patient-specific instruments comparable to conventional TKA? A randomized controlled study of one system.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Dec;471(12):3996-7. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3283-1. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013. PMID: 24046234 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bathis H, Perlick L, Tingart M, Luring C, Grifka J. CT-free computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty versus the conventional technique: radiographic results of 100 cases. Orthopedics. 2004;27:476–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

