Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of an alanine dehydrogenase from Bacillus megaterium WSH-002
- PMID: 23908047
- PMCID: PMC3729178
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309113019672
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of an alanine dehydrogenase from Bacillus megaterium WSH-002
Erratum in
- Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2013 nOV;69(Pt 11):1311
Abstract
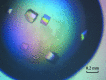
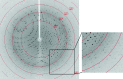
Alanine dehydrogenase (L-AlaDH) from Bacillus megaterium WSH-002 catalyses the NAD⁺-dependent interconversion of L-alanine and pyruvate. The enzyme was expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells and purified with a His6 tag by Ni²⁺-chelating affinity chromatography for X-ray crystallographic analysis. Crystals were grown in a solution consisting of 0.1 M HEPES pH 8.0, 12%(w/v) polyethylene glycol 8000, 8%(v/v) ethylene glycol at a concentration of 15 mg ml⁻¹ purified protein. The crystal diffracted to 2.35 Å resolution and belonged to the trigonal space group R32, with unit-cell parameters a = b = 125.918, c = 144.698 Å.
Keywords: Bacillus megaterium; alanine dehydrogenase.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources