Increased atherosclerotic lesion formation and vascular leukocyte accumulation in renal impairment are mediated by interleukin-17A
- PMID: 23908345
- PMCID: PMC3848055
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301934
Increased atherosclerotic lesion formation and vascular leukocyte accumulation in renal impairment are mediated by interleukin-17A
Abstract
Rationale: Atherosclerosis is a major cause of death in patients with chronic kidney disease. Chronic inflammation of the arterial wall including invasion, proliferation, and differentiation of leukocytes is important in atherosclerotic lesion development. How atherosclerotic inflammation is altered in renal impairment is incompletely understood.
Objective: This study analyzed leukocytes of the atherosclerotic aorta in mice with impaired and normal renal function and studied a mechanism for the alteration in aortic myeloid leukocytes.
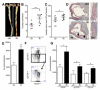
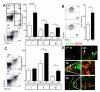
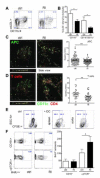
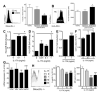
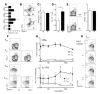
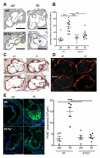
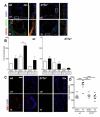
Methods and results: Unilateral nephrectomy significantly decreased glomerular filtration rate and increased atherosclerotic lesion size and aortic leukocyte numbers in 2 murine atherosclerosis models, apolipoprotein E (Apoe(-/-)) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-deficient (LDLr(-/-)) mice. The number of aortic myeloid cells increased significantly. They took-up less oxidized LDL, whereas CD11c expression, interaction with T cells, and aortic T cell proliferation were significantly enhanced in renal impairment. In human peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures, chronic kidney disease serum decreased lipid uptake and increased human leukocyte antigen II (HLA II) expression. Supplementation with interleukin-17A similarly increased HLA II and CD11c expression and impaired oxidized LDL uptake. Interleukin-17A expression was increased in atherosclerotic mice with renal impairment. Ablation of interleukin-17A in LDLr(-/-) mice by lethal irradiation and reconstitution with Il17a(-/-) bone marrow abolished the effect of renal impairment on aortic CD11b(+) myeloid cell accumulation, CD11c expression, and cell proliferation. Atherosclerotic lesion size was decreased to levels observed in normal kidney function.
Conclusions: Kidney function modifies arterial myeloid cell accumulation and phenotype in atherosclerosis. Our results suggest a central role for interleukin-17A in aggravation of vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis in renal impairment.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; interleukin-17; leukocytes; renal insufficiency; vascular inflammation.
Figures
References
-
- Tonelli M, Wiebe N, Culleton B, House A, Rabbat C, Fok M, McAlister F, Garg AX. Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: A systematic review. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN. 2006;17:2034–2047. - PubMed
-
- Astor BC, Hallan SI, Miller ER, 3rd, Yeung E, Coresh J. Glomerular filtration rate, albuminuria, and risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in the us population. American journal of epidemiology. 2008;167:1226–1234. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. The New England journal of medicine. 2004;351:1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Herzog CA, Asinger RW, Berger AK, Charytan DM, Diez J, Hart RG, Eckardt KU, Kasiske BL, McCullough PA, Passman RS, DeLoach SS, Pun PH, Ritz E. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. A clinical update from kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (kdigo) Kidney Int. 2011;80:572–586. - PubMed
-
- Schiffrin EL, Lipman ML, Mann JF. Chronic kidney disease: Effects on the cardiovascular system. Circulation. 2007;116:85–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

