The impact of consultant-delivered multidisciplinary inpatient medical care on patient outcomes
- PMID: 23908501
- PMCID: PMC4954298
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmedicine.13-4-344
The impact of consultant-delivered multidisciplinary inpatient medical care on patient outcomes
Abstract
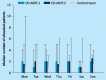
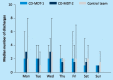
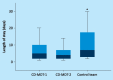
Consultant-delivered care has been shown to improve outcomes for acute medical patients. However, the ideal composition of a medical team to support consultant-delivered care is not clear and little is known about the effect of continuing consultant-delivered care until the patient is discharged. Between December 2011 and April 2012, 260 general medical patients requiring inpatient care were managed by a consultant-delivered multidisciplinary team (CD-MDT) and 150 patients by a standard consultant-led team of trainee doctors. The length of hospital stay was significantly lower for patients managed by a CD-MDT than for those managed by a standard team (4-5 days vs 7 days, p<0.001). No difference between the groups was seen for readmission rates, patient safety or mortality. In conclusion, a CD-MDT is a safe and effective model of inpatient medical care and is associated with a shorter length of hospital stay.
Keywords: Consultant-delivered care; general internal medicine; multidisciplinary team.
Figures
Comment in
-
The impact of consultant-delivered multidisciplinary inpatient medical care on patient outcomes.Clin Med (Lond). 2013 Dec;13(6):631. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.13-6-631. Clin Med (Lond). 2013. PMID: 24298122 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Academy of Medical Royal Colleges The benefits of consultant-delivered care. London: AMRC, 2012. http://aomrc.org.uk/publications/statements/doc_download/9450-the-benefi... [Accessed 7 June 2013].
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

