Assessing the accuracy and certainty in interpreting chest X-rays in the medical division
- PMID: 23908502
- PMCID: PMC4954299
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmedicine.13-4-349
Assessing the accuracy and certainty in interpreting chest X-rays in the medical division
Abstract
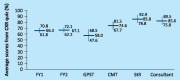
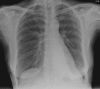
The chest X-ray (CXR) is an important diagnostic tool in diagnosing and monitoring a spectrum of diseases. Despite our universal reliance on the CXR, our ability to confidently diagnose and accurately document our findings can be unreliable. We sought to assess the diagnostic accuracy and certainty of making a diagnosis based on 10 short clinical histories with one CXR each. We conclude from our study that specialist registrars (StRs) and consultants scored the highest marks with the highest average certainty levels. Junior trainees felt least certain about making their diagnosis and were less likely to be correct. We recommend that StRs and consultants review all the CXRs requested to ensure accuracy of diagnosis. There also needs to be discussion with the Joint Royal Colleges of Physicians Training Board (JRCPTB) about the need of including a separate CXR competency as part of a trainee's generic curriculum on the e-portfolio, something which is currently lacking.
Keywords: Chest X-ray; education; radiology; reporting; training.
Figures

References
-
- Kanne JP, Thoongsuwan N, Stern EJ. Common errors and pitfalls in interpretation of the adult chest radiograph. Clin Pulm Med 2005;12:97-114. 10.1097/01.cpm.0000156704.33941.e2 - DOI
-
- Weiner SN. Radiology by non-radiologists: is report documentation adequate? Am J Manag Care 2005;11:781-5. - PubMed
-
- Royal College of Radiologists Clinical radiology: a workforce in crisis. London: RCR, 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

