p53-stabilizing agent CP-31398 prevents growth and invasion of urothelial cancer of the bladder in transgenic UPII-SV40T mice
- PMID: 23908596
- PMCID: PMC3730047
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.13704
p53-stabilizing agent CP-31398 prevents growth and invasion of urothelial cancer of the bladder in transgenic UPII-SV40T mice
Abstract
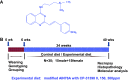
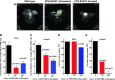
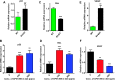
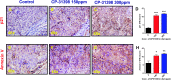
The high prevalence of bladder cancer and its recurrence make it an important target for chemoprevention. About half of invasive urothelial tumors have mutations in p53. We determined the chemopreventive efficacy of a p53-stabilizing agent, CP-31398, in a transgenic UPII-SV40T mouse model of bladder transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) that strongly resembles human TCC. After genotyping, six-week-old UPII-SV40T mice (n = 30/group) were fed control (AIN-76A) or experimental diets containing 150 or 300 ppm of CP-31398 for 34 weeks. Progression of bladder cancer growth was monitored by magnetic resonance imaging. At 40 weeks of age, all mice were killed; urinary bladders were collected to determine weights, tumor incidence, and histopathology. There was a significant increase in bladder weights of transgenic versus wild-type mice (male: 140.2 mg vs 27.3 mg, P < .0001; female: 34.2 mg vs 14.8 mg, P < .0001). A significant decrease in the bladder tumor weights (by 68.6-80.2%, P < .0001 in males and by 36.9-55.3%, P < .0001 in females) was observed in CP-31398-treated mice. Invasive papillary TCC incidence was 100% in transgenic mice fed control diet. Both male and female mice exposed to CP-31398 showed inhibition of invasive TCC. CP-31398 (300 ppm) completely blocked invasion in female mice. Molecular analysis of the bladder tumors showed an increase in apoptosis markers (p53, p21, Bax, and Annexin V) with a decrease in vascular endothelial growth factor in transgenic mice fed CP-31398. These results suggest that p53-modulating agents can serve as potential chemopreventive agents for bladder TCC.
Figures

References
-
- American Cancer Society (ACS), author Cancer Facts & Figures 2013. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2013.
-
- Schalken JA, van Moorselaar RJ, Bringuier PP, Debruyne FM. Critical review of the models to study the biologic progression of bladder cancer. Semin Surg Oncol. 1992;8:274–278. - PubMed
-
- Steinberg GD, Trump DL, Cummings KB. Metastatic bladder cancer. Natural history, clinical course, and consideration for treatment. Urol Clin North Am. 1992;19:735–746. - PubMed
-
- Dalbagni G, Presti J, Reuter V, Fair WR, Cordon-Cardo C. Genetic alterations in bladder cancer. Lancet. 1993;342:469–471. - PubMed
-
- Spruck CH, Ohneseit PF, Gonzalez-Zulueta M, Esrig D, Miyao N, Tsai YC, Lerner SP, Schmutte C, Yang AS, Cote R, et al. Two molecular pathways to transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Res. 1994;54:784–788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
