A phylogenomic and molecular signature based approach for characterization of the phylum Spirochaetes and its major clades: proposal for a taxonomic revision of the phylum
- PMID: 23908650
- PMCID: PMC3726837
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00217
A phylogenomic and molecular signature based approach for characterization of the phylum Spirochaetes and its major clades: proposal for a taxonomic revision of the phylum
Erratum in
-
Erratum: A phylogenomic and molecular signature based approach for characterization of the Phylum Spirochaetes and its major clades: proposal for a taxonomic revision of the phylum.Front Microbiol. 2013 Oct 31;4:322. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00322. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24198815 Free PMC article.
Abstract
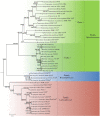
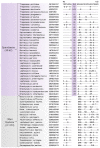
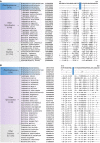
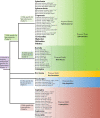
The Spirochaetes species cause many important diseases including syphilis and Lyme disease. Except for their containing a distinctive endoflagella, no other molecular or biochemical characteristics are presently known that are specific for either all Spirochaetes or its different families. We report detailed comparative and phylogenomic analyses of protein sequences from Spirochaetes genomes to understand their evolutionary relationships and to identify molecular signatures for this group. These studies have identified 38 conserved signature indels (CSIs) that are specific for either all members of the phylum Spirochaetes or its different main clades. Of these CSIs, a 3 aa insert in the FlgC protein is uniquely shared by all sequenced Spirochaetes providing a molecular marker for this phylum. Seven, six, and five CSIs in different proteins are specific for members of the families Spirochaetaceae, Brachyspiraceae, and Leptospiraceae, respectively. Of the 19 other identified CSIs, 3 are uniquely shared by members of the genera Sphaerochaeta, Spirochaeta, and Treponema, whereas 16 others are specific for the genus Borrelia. A monophyletic grouping of the genera Sphaerochaeta, Spirochaeta, and Treponema distinct from the genus Borrelia is also strongly supported by phylogenetic trees based upon concatenated sequences of 22 conserved proteins. The molecular markers described here provide novel and more definitive means for identification and demarcation of different main groups of Spirochaetes. To accommodate the extensive genetic diversity of the Spirochaetes as revealed by different CSIs and phylogenetic analyses, it is proposed that the four families of this phylum should be elevated to the order level taxonomic ranks (viz. Spirochaetales, Brevinematales ord. nov., Brachyspiriales ord. nov., and Leptospiriales ord. nov.). It is further proposed that the genera Borrelia and Cristispira be transferred to a new family Borreliaceae fam. nov. within the order Spirochaetales.
Keywords: Borreliaceae; Brachyspiriales; Leptospiriales; Spirochaetaceae; Spirochaetes; Spirochaetes phylogeny and taxonomy; conserved signature indels; molecular signatures.
Figures




References
-
- Abt B., Göker M., Scheuner C., Han C., Lu M., Misra M., et al. (2013). Genome sequence of the thermophilic fresh-water bacterium Spirochaeta caldaria type strain (H1 T), reclassification of Spirochaeta caldaria and Spirochaeta stenostrepta in the genus Treponema as Treponema caldaria comb. nov., Treponema stenostrepta comb. nov., and Treponema zuelzerae comb. nov., and emendation of the genus Treponema. Stand. Genomic Sci. 8 [Epub ahead of print]. 10.4056/sigs.3096473 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abt B., Han C., Scheuner C., Lu M., Lapidus A., Nolan M., et al. (2012). Complete genome sequence of the termite hindgut bacterium Spirochaeta coccoides type strain (SPN1T), reclassification in the genus Sphaerochaeta as Sphaerochaeta coccoides comb. nov. and emendations of the family Spirochaetaceae and the genus Sphaerochaeta. Stand. Genomic Sci. 6, 194 10.4056/sigs.2796069 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

