Prostate magnetic resonance imaging at 3 Tesla: Is administration of hyoscine-N-butyl-bromide mandatory?
- PMID: 23908696
- PMCID: PMC3730080
- DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i7.259
Prostate magnetic resonance imaging at 3 Tesla: Is administration of hyoscine-N-butyl-bromide mandatory?
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the value of administration of hyoscine-N-butyl-bromide (HBB) for image quality magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the prostate.
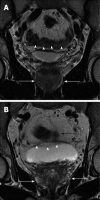
Methods: Seventy patients were retrospectively included in the study. Thirty-five patients were examined with administration of 40 milligrams of HBB (Buscopan(®); Boehringer, Ingelheim, Germany); 35 patients were examined without HBB. A multiparametric MRI protocol was performed on a 3.0 Tesla scanner without using an endorectal coil. The following criteria were evaluated independently by two experienced radiologists on a five-point Likert scale: anatomical details (delineation between peripheral and transitional zone of the prostate, visualisation of the capsule, depiction of the neurovascular bundles); visualisation of lymph nodes; motion related artefacts; and overall image quality.
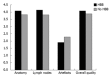
Results: Comparison of anatomical details between the two cohorts showed no statistically significant difference (3.9 ± 0.7 vs 4.0 ± 0.9, P = 0.54, and 3.8 ± 0.7 vs 4.2 ± 0.6, P = 0.07) for both readers. There was no significant advantage regarding depiction of local and iliac lymph nodes (3.9 ± 0.6 vs 4.2 ± 0.6, P = 0.07, and 3.8 ± 0.9 vs 4.1 ± 0.8, P = 0.19). Motion artefacts were rated as "none" to "few" in both groups and showed no statistical difference (2.3 ± 1.0 vs 1.9 ± 0.9, P = 0.19, and 2.3 ± 1.1 vs 1.9 ± 0.7, P = 0.22). Overall image quality was rated "good" in average for both cohorts without significant difference (4.0 ± 0.6 vs 4.0 ± 0.9, P = 0.78, and 3.8 ± 0.8 vs 4.2 ± 0.6, P = 0.09).
Conclusion: The results demonstrated no significant effect of HBB administration on image quality. The study suggests that use of HBB is not mandatory for MRI of the prostate at 3.0 Tesla.
Keywords: 3 Tesla; Buscopan; Butylscopolamine; Magnetic resonance imaging; Motion artefacts; Prostate cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Dosdá R, Martí-Bonmatí L, Ronchera-Oms CL, Mollá E, Arana E. Effect of subcutaneous butylscopolamine administration in the reduction of peristaltic artifacts in 1.5-T MR fast abdominal examinations. Eur Radiol. 2003;13:294–298. - PubMed
-
- Wagner M, Rief M, Busch J, Scheurig C, Taupitz M, Hamm B, Franiel T. Effect of butylscopolamine on image quality in MRI of the prostate. Clin Radiol. 2010;65:460–464. - PubMed
-
- Bloch BN, Rofsky NM, Baroni RH, Marquis RP, Pedrosa I, Lenkinski RE. 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate with combined pelvic phased-array and endorectal coils; Initial experience(1) Acad Radiol. 2004;11:863–867. - PubMed
-
- Sosna J, Pedrosa I, Dewolf WC, Mahallati H, Lenkinski RE, Rofsky NM. MR imaging of the prostate at 3 Tesla: comparison of an external phased-array coil to imaging with an endorectal coil at 1.5 Tesla. Acad Radiol. 2004;11:857–862. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

