Two cases of severe pneumonia after the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake
- PMID: 23908944
- PMCID: PMC3729095
- DOI: 10.5365/WPSAR.2012.3.2.002
Two cases of severe pneumonia after the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake
Abstract
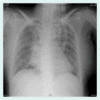
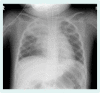
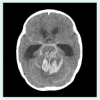
In 2011, during the Great East Japan Earthquake and tsunami, 90% of victims died from drowning. We report on two tsunami survivors with severe pneumonia potentially caused by Legionella pneumophila. Both victims aspirated a large quantity of contaminated water; sand, mud and a variety of microbes were thought to have entered into their lower respiratory tracts. One patient had a mycotic intracranial aneurysm; the other patient had co-infections with several organisms, including Scedosporium species. Although scedosporiosis is a relatively rare infectious disease, symptoms are progressive and prognosis is poor. These pathogens are not specific for tsunami lung, but are reported causative agents for pneumonia after near-drowning.
Figures
References
-
- Jeremijenko A, McLaws ML, Kosasih H. A tsunami related tetanus epidemic in Aceh, Indonesia. Asia-Pacific Journal of Public Health. 2007;19(Spec No):40–4. - PubMed
-
- Allworth AM. Tsunami lung: a necrotising pneumonia in survivors of the Asian tsunami. The Medical Journal of Australia. 2005;182:364. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
