Lessons learned from the development of health applications in a tertiary hospital
- PMID: 23909863
- PMCID: PMC3934672
- DOI: 10.1089/tmj.2013.0192
Lessons learned from the development of health applications in a tertiary hospital
Abstract
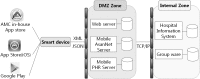
Background: Adoption of smart devices for hospital use has been increasing with the development of health applications (apps) for patient point-of-care and hospital management. To promote the use of health apps, we describe the lessons learned from developing 12 health apps in the largest tertiary hospital in Korea.
Materials and methods: We reviewed and analyzed 12 routinely used apps in three categories-Smart Clinic, Smart Patient, and Smart Hospital-based on target users and functions. The log data for each app were collected from the date of release up until December 2012.
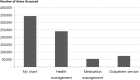
Results: Medical personnel accessed a mobile electronic medical record app classified as Smart Clinic an average of 452 times per day. Smart Hospital apps are actively used to communicate with each other. Patients logged on to a mobile personal health record app categorized as Smart Patient an average of 222 times per day. As the mobile trend, the choice of supporting operating system (OS) is more difficult. By developing these apps, a monitoring system is needed for evaluation.
Conclusions: We described the lessons learned regarding OS support, device choice, and developmental strategy. The OS can be chosen according to market share or hospital strategic plan. Smartphones were favored compared with tablets. Alliance with an information technology company can be the best way to develop apps. Health apps designed for smart devices can be used to improve healthcare. However, to develop health apps, hospitals must define their future goals and carefully consider all the aspects.
Figures






References
-
- World Health Organization Global Observatory for eHealth Series, Vol. 3: mHealth: New horizons for health through mobile technologies. Geneva: WHO Press, 2011
-
- Expect rapid growth for telehealth, mHealth markets Available at www.cmio.net/index.php?option=com_articles&view=article&id=34805:expect-... (last accessed April22, 2013)
-
- PricewaterhouseCoopers Emerging mHealth: Paths for growth. Available at www.pwc.com/en_GX/gx/healthcare/mhealth/assets/pwc-emerging-mhealth-full... (last accessed April29, 2013)
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
