Increase of phosphatase and tensin homolog by silymarin to inhibit human pharynx squamous cancer
- PMID: 23909904
- PMCID: PMC3778994
- DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2012.2534
Increase of phosphatase and tensin homolog by silymarin to inhibit human pharynx squamous cancer
Abstract
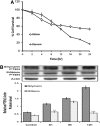
Silymarin is an active principle from the seeds of the milk thistle plant and is widely used as a hepatoprotective gent due to its antioxidant-like activity. In the present study, we evaluated the potential efficacy of silymarin against oral cancer and investigated its possible mechanism of action. Cell viability assay and western blotting analyses were used to identify silymarin-induced apoptotic cell death in human pharynx squamous cell carcinoma (FaDu) cells. The short interfering RNA (siRNA) is used to confirm the role of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) in silymarin-induced apoptosis. Treatment of FaDu cells with silymarin resulted in a significant decrease in cell viability (up to 70%). Silymarin inhibited the phosphorylation of Akt (over 10-fold) with an increase in expression of PTEN (five to sixfold). Consequently, the level of Bcl-2 expression was decreased five to sixfold and caspase 3 activated to induce apoptosis. Treatment with siRNA specific to PTEN gene diminished the action of silymarin. The results suggest that silymarin inhibits the Akt signaling pathway by increasing PTEN expression in FaDu cells and directly affects Bcl-2 family members. Also, we demonstrated the inhibitory activity of silymarin for oral cancer is related to cell survival. These mechanisms may in part explain the actions of silymarin and provide a rationale for the development of silymarin as an anticancer agent.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Silymarin inhibits cervical cancer cell through an increase of phosphatase and tensin homolog.Phytother Res. 2012 May;26(5):709-15. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3618. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Phytother Res. 2012. PMID: 22016029
-
Silymarin induces insulin resistance through an increase of phosphatase and tensin homolog in Wistar rats.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 3;9(1):e84550. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084550. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24404172 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis-induced effects of extract from Artemisia annua Linné by modulating PTEN/p53/PDK1/Akt/ signal pathways through PTEN/p53-independent manner in HCT116 colon cancer cells.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Apr 28;17(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1702-7. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28454566 Free PMC article.
-
Silybum marianum (milk thistle) and its main constituent, silymarin, as a potential therapeutic plant in metabolic syndrome: A review.Phytother Res. 2018 Oct;32(10):1933-1949. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6153. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Phytother Res. 2018. PMID: 30015401 Review.
-
Silymarin antiproliferative and apoptotic effects: Insights into its clinical impact in various types of cancer.Phytother Res. 2019 Nov;33(11):2849-2861. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6470. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Phytother Res. 2019. PMID: 31407422 Review.
Cited by
-
Limosilactobacillus reuteri SXDT-32-derived shikimic acid protects against colonic inflammation in piglets by inhibiting the PI3K-Akt pathway.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025 Jun 13;16(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s40104-025-01221-w. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40514681 Free PMC article.
-
Silymarin suppresses HepG2 hepatocarcinoma cell progression through downregulation of Slit-2/Robo-1 pathway.Pharmacol Rep. 2020 Feb;72(1):199-207. doi: 10.1007/s43440-019-00040-x. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Pharmacol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32016841
-
Low-Frequency Magnetic Fields (LF-MFs) Inhibit Proliferation by Triggering Apoptosis and Altering Cell Cycle Distribution in Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 22;21(8):2952. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082952. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32331350 Free PMC article.
-
Increase in apoptosis by combination of metformin with silibinin in human colorectal cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr 14;21(14):4169-77. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4169. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25892866 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Silymarin in Cancer Treatment: Facts, Hypotheses, and Questions.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2022 Jan-Dec;27:2515690X211068826. doi: 10.1177/2515690X211068826. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 35018864 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kroll DJ. Shaw HS. Oberlies NH. Milk thistle nomenclature: why it matters in cancer research and pharmacokinetic studies. Integr Cancer Ther. 2007;6:110–119. - PubMed
-
- Feher J. Lengyel G. [Silymarin in the treatment of chronic liver diseases: past and future] Orv Hetil. 2008;149:2413–2418. - PubMed
-
- Saller R. Meier R. Brignoli R. The use of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs. 2001;61:2035–2063. - PubMed
-
- Flora K. Hahn M. Rosen H. Benner K. Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) for the therapy of liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:139–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

