Coenzyme Q10 and male infertility: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 23912751
- PMCID: PMC3800531
- DOI: 10.1007/s10815-013-0047-5
Coenzyme Q10 and male infertility: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of coenzyme Q10 treatments in male infertility, specifically in these parameters: live birth and pregnancy rates, CoQ10 seminal concentration, sperm concentration, and sperm motility.
Materials and methods: Systematic review and meta-analysis in male infertility patients with CoQ10 oral treatments. Three trials were included: 149 males in CoQ10 group and 147 males in placebo group.
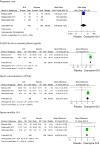
Results: None of the included trials provided any data regarding live births. The results of this meta-analysis show that supplementing infertile men with CoQ10 does not increase pregnancy rates. The analysis showed, among patients receiving CoQ10 treatment, a statistically significant increase in: CoQ10 seminal concentration (RR 49.55, 95 % CI 46.44 to 52.66, I(2) = 17 %), sperm concentration (RR 5.33, 95 % CI 4.18 to 6.47, I(2) = 58 %), and sperm motility (RR 4.50, 95 % CI 3.92 to 5.08, I(2) = 0 %)
Conclusion: There is no evidence in the literature that CoQ10 increases either live birth or pregnancy rates, but there is a global improvement in sperm parameters. Adequately powered, robust trials of individual and combination antioxidant therapies are required to guide clinical practice.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: coenzyme Q10 and male infertility: a meta-analysis.J Urol. 2014 Mar;191(3):753. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.11.071. Epub 2013 Nov 28. J Urol. 2014. PMID: 24522063 No abstract available.
References
-
- Auger J, Eustache F, Andersen AG, Irvine DS, Jorgensen N, Skakkebaek NE, et al. Sperm morphological defects related to environment, lifestyle and medical history of 1001 male partners of pregnant women from four European cities. Hum Reprod. 2001;16:2710–7. doi: 10.1093/humrep/16.12.2710. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical