Notch2-dependent classical dendritic cells orchestrate intestinal immunity to attaching-and-effacing bacterial pathogens
- PMID: 23913046
- PMCID: PMC3788683
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2679
Notch2-dependent classical dendritic cells orchestrate intestinal immunity to attaching-and-effacing bacterial pathogens
Abstract
Defense against attaching-and-effacing bacteria requires the sequential generation of interleukin 23 (IL-23) and IL-22 to induce protective mucosal responses. Although CD4(+) and NKp46(+) innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are the critical source of IL-22 during infection, the precise source of IL-23 is unclear. We used genetic techniques to deplete mice of specific subsets of classical dendritic cells (cDCs) and analyzed immunity to the attaching-and-effacing pathogen Citrobacter rodentium. We found that the signaling receptor Notch2 controlled the terminal stage of cDC differentiation. Notch2-dependent intestinal CD11b(+) cDCs were an obligate source of IL-23 required for survival after infection with C. rodentium, but CD103(+) cDCs dependent on the transcription factor Batf3 were not. Our results demonstrate a nonredundant function for CD11b(+) cDCs in the response to pathogens in vivo.
Figures


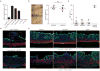
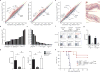
Comment in
-
DCs: a dual bridge to protective immunity.Nat Immunol. 2013 Sep;14(9):890-1. doi: 10.1038/ni.2693. Nat Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23959179 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mangan PR, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta induces development of the T(H)17 lineage. Nature. 2006;441:231–234. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y, et al. Interleukin-22 mediates early host defense against attaching and effacing bacterial pathogens. Nat Med. 2008;14:282–289. - PubMed
-
- Spits H, Di Santo JP. The expanding family of innate lymphoid cells: regulators and effectors of immunity and tissue remodeling. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:21–27. - PubMed
-
- Colonna M. Interleukin-22-producing natural killer cells and lymphoid tissue inducer-like cells in mucosal immunity. Immunity. 2009;31:15–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK071619/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI095542-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE021255-01/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007317/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA91842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM055479/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA091842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MOP 67157/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- U01 AI095542/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM55479/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE021255/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK064798/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI076427-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076427/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

