ClpB1 overproduction in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 increases tolerance to rapid heat shock
- PMID: 23913426
- PMCID: PMC3811215
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01661-13
ClpB1 overproduction in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 increases tolerance to rapid heat shock
Abstract
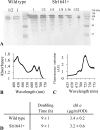
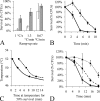
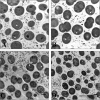
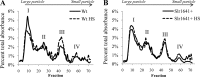
ClpB1 is a heat shock protein known to disaggregate large protein complexes. Constitutive, 16-fold ClpB1 overproduction in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 increased cell survival by 20-fold when cultures were heated quickly (1°C/s) to 50°C and delayed cell death by an average of 3 min during incubation at high temperatures (>46°C). Cooverexpression of ClpB1 and another heat shock protein, DnaK2, further increased cell survival. According to immunocytochemistry results, ClpB1 is dispersed throughout the cytoplasm but is concentrated in specific areas and is more prevalent near thylakoid membranes. However, ClpB1 overproduction does not lead to a change in the morphology, chlorophyll content, or photosystem ratio. Whereas electron microscopy demonstrated that apparent protein aggregation occurred after heat treatment in the control strain, protein aggregate size was maintained in the ClpB1 overexpresser. Constitutive ClpB1 overproduction allows an earlier response to heat shock and protects from rapid heating of cultures.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The heat shock response of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 analysed by transcriptomics and proteomics.J Exp Bot. 2006;57(7):1573-8. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erj148. Epub 2006 Mar 30. J Exp Bot. 2006. PMID: 16574748
-
Three different DnaK proteins are functionally expressed in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Microbiology (Reading). 2007 Jun;153(Pt 6):1828-1841. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/005876-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2007. PMID: 17526840
-
HSP16.6 is involved in the development of thermotolerance and thylakoid stability in the unicellular cyanobacterium, Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Curr Microbiol. 2000 Apr;40(4):283-7. doi: 10.1007/s002849910056. Curr Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10688700
-
A small heat-shock protein confers stress tolerance and stabilizes thylakoid membrane proteins in cyanobacteria under oxidative stress.Arch Microbiol. 2009 Apr;191(4):319-28. doi: 10.1007/s00203-009-0457-z. Epub 2009 Jan 24. Arch Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19169670
-
Effects of high light on transcripts of stress-associated genes for the cyanobacteria Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and Prochlorococcus MED4 and MIT9313.Microbiology (Reading). 2004 May;150(Pt 5):1271-1281. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27014-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2004. PMID: 15133090
Cited by
-
Escherichia coli AraJ boosts utilization of arabinose in metabolically engineered cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.AMB Express. 2021 Aug 13;11(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13568-021-01277-7. AMB Express. 2021. PMID: 34387784 Free PMC article.
-
Highlights from the Indo-US workshop "Cyanobacteria: molecular networks to biofuels" held at Lonavala, India during December 16-20, 2012.Photosynth Res. 2013 Nov;118(1-2):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s11120-013-9933-z. Photosynth Res. 2013. PMID: 24142037
-
Application of Cyanobacteria as Chassis Cells in Synthetic Biology.Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 5;12(7):1375. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071375. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State-of-the-Art Genetic Modalities to Engineer Cyanobacteria for Sustainable Biosynthesis of Biofuel and Fine-Chemicals to Meet Bio-Economy Challenges.Life (Basel). 2019 Jun 27;9(3):54. doi: 10.3390/life9030054. Life (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31252652 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pulz O, Gross W. 2004. Valuable products from biotechnology of microalgae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 65:635–648 - PubMed
-
- Machado IMP, Atsumi S. 2012. Cyanobacterial biofuel production. J. Biotechnol. 162:50–56 - PubMed
-
- Kaneko T, Sato S, Kotani H, Tanaka A, Asamizu E, Nakamura Y, Miyajima N, Hirosawa M, Sugiura M, Sasamoto S, Kimura T, Hosouchi T, Matsuno A, Muraki A, Nakazaki N, Naruo K, Okumura S, Shimpo S, Takeuchi C, Wada T, Watanabe A, Yamada M, Yasuda M, Tabata S. 1996. Sequence analysis of the genome of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. II. Sequence determination of the entire genome and assignment of potential protein-coding regions. DNA Res. 3:109–136 - PubMed
-
- Vermaas W. 1996. Molecular genetics of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: principles and possible biotechnology applications. J. Appl. Phycol. 8:263–273
-
- Yang C, Hua Q, Shimizu K. 2002. Metabolic flux analysis in Synechocystis using isotope distribution from 13C-labeled glucose. Metab. Eng. 4:202–216 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

