Inhibiting glycogen synthesis prevents Lafora disease in a mouse model
- PMID: 23913475
- PMCID: PMC3823666
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.23899
Inhibiting glycogen synthesis prevents Lafora disease in a mouse model
Abstract
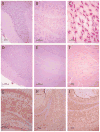
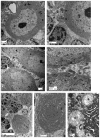
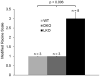
Lafora disease (LD) is a fatal progressive myoclonus epilepsy characterized neuropathologically by aggregates of abnormally structured glycogen and proteins (Lafora bodies [LBs]), and neurodegeneration. Whether LBs could be prevented by inhibiting glycogen synthesis and whether they are pathogenic remain uncertain. We genetically eliminated brain glycogen synthesis in LD mice. This resulted in long-term prevention of LB formation, neurodegeneration, and seizure susceptibility. This study establishes that glycogen synthesis is requisite for LB formation and that LBs are pathogenic. It opens a therapeutic window for potential treatments in LD with known and future small molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthesis.
© 2013 American Neurological Association.
Figures
References
-
- Lafora GR, Glueck B. Beitrag zur Histopathologie der myoklonischen Epilepsie. Zeitschrift Gesamte Neurologische Psychiatrie. 1911;6:1–14.
-
- Sakai M, Austin J, Witmer F, Trueb L. Studies in myoclonus epilepsy (Lafora body form). II. Polyglucosans in the systemic deposits of myoclonus epilepsy and in corpora amylacea. Neurology. 1970 Feb;20(2):160–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

