Aging and chronic kidney disease: the impact on physical function and cognition
- PMID: 23913934
- PMCID: PMC4017829
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glt109
Aging and chronic kidney disease: the impact on physical function and cognition
Abstract
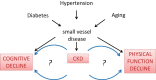
Evidence has recently been building that the presence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is an independent contributor to decline in physical and cognitive functions in older adults. CKD affects 45% of persons older than 70 years of age and can double the risk for physical impairment, cognitive dysfunction, and frailty. To increase awareness of this relatively new concept of CKD as a risk factor for accelerated aging, we review studies on the association of CKD with physical function, frailty, and cognitive function. We also present a summary of the proposed mechanisms for these associations.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Cognitive function.; Frailty; Physical function.
Figures
References
-
- Feng L, Yap KB, Yeoh LY, Ng TP. Kidney function and cognitive and functional decline in elderly adults: findings from the Singapore longitudinal aging study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60(7):1208–1214 - PubMed
-
- Kurella M, Chertow GM, Fried LF, et al. Chronic kidney disease and cognitive impairment in the elderly: the health, aging, and body composition study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16(7):2127–2133 - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298(17):2038–2047 - PubMed
-
- Fried LP, Ferrucci L, Darer J, Williamson JD, Anderson G. Untangling the concepts of disability, frailty, and comorbidity: implications for improved targeting and care. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2004;59(3):255–263 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

