Polymeric Nanomedicines Based on Poly(lactide) and Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)
- PMID: 23914135
- PMCID: PMC3728009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cossms.2013.01.001
Polymeric Nanomedicines Based on Poly(lactide) and Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)
Abstract
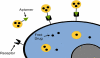
Small molecule chemotherapeutics often have undesired physiochemical and pharmacological properties, such as low solubility, severe side effect and narrow therapeutic index. To address these challenges, polymeric nanomedicine drug delivery technology has been routinely employed, in particular with the use of biodegradable and biocompatible polyesters, such as poly(lactide) (PLA) and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA). Here we review the development and use of PLA and PLGA for the delivery of chemotherapeutic agents in the forms of polymer-drug conjugates and nanoconjugates.
Keywords: Cancer; PLA; PLGA; aptamer; cancer targeting; chemotherapeutics; drug delivery; nanoconjugates; nanomedicine; poly(lactide); poly(lactide-co-glycolide); polymer-drug conjugates.
Figures
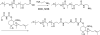
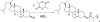

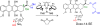
Similar articles
-
The manufacturing techniques of various drug loaded biodegradable poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) devices.Biomaterials. 2000 Dec;21(23):2475-90. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(00)00115-0. Biomaterials. 2000. PMID: 11055295 Review.
-
Vancomycin release from poly(D,L-lactide) and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) disks.J Microencapsul. 2002 Jan-Feb;19(1):83-94. doi: 10.1080/02652040110065404. J Microencapsul. 2002. PMID: 11811762
-
Physicomechanical properties of biodegradable poly(D,L-lactide) and poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) films in the dry and wet states.J Pharm Sci. 2000 Dec;89(12):1558-66. doi: 10.1002/1520-6017(200012)89:12<1558::aid-jps6>3.0.co;2-8. J Pharm Sci. 2000. PMID: 11042603
-
Synthesis of uniform poly(d,l-lactide) and poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres using a microfluidic chip for comparison.Electrophoresis. 2014 Feb;35(2-3):316-22. doi: 10.1002/elps.201300185. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Electrophoresis. 2014. PMID: 23857679
-
Pharmacokinetic Consequences of PLGA Nanoparticles in Docetaxel Drug Delivery.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2017;5(1):3-23. doi: 10.2174/2211738505666161230110108. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28948907 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted delivery system of nanobiomaterials in anticancer therapy: from cells to clinics.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:814208. doi: 10.1155/2014/814208. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24672796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Formation of Self-Assembled Nanoparticles Loaded with Doxorubicin and d-Limonene for Cancer Therapy.ACS Omega. 2022 Nov 13;7(46):42096-42104. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04238. eCollection 2022 Nov 22. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36440142 Free PMC article.
-
N-acetylcysteine-PLGA nano-conjugate: effects on cellular toxicity and uptake of gadopentate dimeglumine.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020 Aug;14(6):470-478. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2019.0374. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32755956 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Ultrathin Orsiro Biodegradable Polymer Drug-eluting Stent in the Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease.Heart Int. 2019 Dec 23;13(2):17-24. doi: 10.17925/HI.2019.13.2.17. eCollection 2019. Heart Int. 2019. PMID: 36274821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multifunctional biodegradable brush polymer-drug conjugate for paclitaxel/gemcitabine co-delivery and tumor imaging.Nanoscale Adv. 2019;1(7):2761-2771. doi: 10.1039/c9na00282k. Epub 2019 May 27. Nanoscale Adv. 2019. PMID: 32864564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Langer R. Drug delivery and targeting. Nature. 1998;392(6679):5–10. - PubMed
-
- Collins I, Workman P. New approaches to molecular cancer therapeutics. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2(12):689–700. - PubMed
-
- Duncan R. Polymer conjugates as anticancer nanomedicines. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(9):688–701. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari M. Cancer nanotechnology: Opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(3):161–71. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
