Promise for plant pest control: root-associated pseudomonads with insecticidal activities
- PMID: 23914197
- PMCID: PMC3728486
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00287
Promise for plant pest control: root-associated pseudomonads with insecticidal activities
Abstract
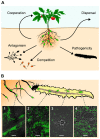
Insects are an important and probably the most challenging pest to control in agriculture, in particular when they feed on belowground parts of plants. The application of synthetic pesticides is problematic owing to side effects on the environment, concerns for public health and the rapid development of resistance. Entomopathogenic bacteria, notably Bacillus thuringiensis and Photorhabdus/Xenorhabdus species, are promising alternatives to chemical insecticides, for they are able to efficiently kill insects and are considered to be environmentally sound and harmless to mammals. However, they have the handicap of showing limited environmental persistence or of depending on a nematode vector for insect infection. Intriguingly, certain strains of plant root-colonizing Pseudomonas bacteria display insect pathogenicity and thus could be formulated to extend the present range of bioinsecticides for protection of plants against root-feeding insects. These entomopathogenic pseudomonads belong to a group of plant-beneficial rhizobacteria that have the remarkable ability to suppress soil-borne plant pathogens, promote plant growth, and induce systemic plant defenses. Here we review for the first time the current knowledge about the occurrence and the molecular basis of insecticidal activity in pseudomonads with an emphasis on plant-beneficial and prominent pathogenic species. We discuss how this fascinating Pseudomonas trait may be exploited for novel root-based approaches to insect control in an integrated pest management framework.
Keywords: Bacillus; Pseudomonas; biocontrol; entomopathogens; insecticidal; plant-associated; rhizosphere; toxins.
Figures
References
-
- Almario J., Prigent-Combaret C., Muller D., Moënne-Loccoz Y. (2013) Effect of clay mineralogy on iron bioavailability and rhizosphere transcription of 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol biosynthetic genes in biocontrol Pseudomonas protegens Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 26 566–574 10.1094/MPMI-11-12-0274-R - DOI - PubMed
-
- Apidianakis Y., Mindrinos M. N., Xiao W., Lau G. W., Baldini R. L., Davis R. W. et al. (2005). Profiling early infection responses: Pseudomonas aeruginosa eludes host defenses by suppressing antimicrobial peptide gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 2573–25781 10.1073/pnas.0409588102 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arias-Cordero E., Ping L., Reichwald K., Delb H., Platzer M., Boland W. (2012) Comparative evaluation of the gut microbiota associated with the below- and above-ground life stages (larvae and beetles) of the forest cockchafer, Melolontha hippocastani. PLoS ONE 7: e51557 10.1371/journal.pone.0051557 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

