Environmental stress and transposon transcription in the mammalian brain
- PMID: 23914311
- PMCID: PMC3681740
- DOI: 10.4161/mge.24555
Environmental stress and transposon transcription in the mammalian brain
Abstract
We recently reported that acute stress causes a substantial upregulation of the epigenetic mark, Histone H3 Lysine 9 Trimethyl (H3K9me3) in the rat hippocampus within an hour of acute stress exposure. To determine the function of this change we used ChIP-sequencing to determine where this silencing mark was being localized. We found that it showed a strong bias toward localization at more active classes of retrotransposable elements and away from genes. Further, we showed that the change was functional in that it reduced transcription of some of these elements (notably the endogenous retrovirus IAP and the B2 SINE). In this commentary we examine these results, which appear to describe a selective genomic stress response and relate it to human health and disease, particularly stress related maladies such as Post-traumatic Stress Disorder, which have recently been shown to have both epigenetic elements in their causation as well as differences in epigenetic marking of retrotransposons in human patients.
Keywords: chromatin; corticosteroid; epigenetic; heterochromatin; hippocampus; post-traumatic stress disorder.
Figures
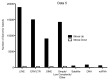
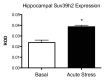
Comment on
- Hunter RG, Murakami G, Dewell S, Seligsohn M, Baker ME, Datson NA, et al. Acute stress and hippocampal histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation, a retrotransposon silencing response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:17657–62. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215810109.
Similar articles
-
Corticosterone dynamically regulates retrotransposable element expression in the rat hippocampus and C6 cells.Neurobiol Stress. 2021 Sep 13;15:100397. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100397. eCollection 2021 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2021. PMID: 34584909 Free PMC article.
-
Acute stress and hippocampal histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation, a retrotransposon silencing response.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 23;109(43):17657-62. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215810109. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23043114 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive patterns of epigenetic marks are associated with promoter regions of mouse LINE-1 and LTR retrotransposons.Mob DNA. 2013 Dec 2;4(1):27. doi: 10.1186/1759-8753-4-27. Mob DNA. 2013. PMID: 24289137 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenomics in stress tolerance of plants under the climate change.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6201-6216. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08539-6. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37294468 Review.
-
Epigenetic landscape of amphetamine and methamphetamine addiction in rodents.Epigenetics. 2015;10(7):574-80. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1055441. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26023847 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bridging the Gap Between Environmental Adversity and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: The Role of Transposable Elements.Front Genet. 2022 May 25;13:813510. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.813510. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35711940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A single whole-body low dose X-irradiation does not affect L1, B1 and IAP repeat element DNA methylation longitudinally.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 27;9(3):e93016. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093016. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24676381 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of stress in the brain.Nat Neurosci. 2015 Oct;18(10):1353-63. doi: 10.1038/nn.4086. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Nat Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26404710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal Immune Activation and Enriched Environments Impact B2 SINE Expression in Stress Sensitive Brain Regions of Rodent Offspring.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 1;14(4):858. doi: 10.3390/genes14040858. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107616 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosterone dynamically regulates retrotransposable element expression in the rat hippocampus and C6 cells.Neurobiol Stress. 2021 Sep 13;15:100397. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100397. eCollection 2021 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2021. PMID: 34584909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selye H. A Syndrome Produced by Diverse Nocuous Agents. Nature. 1936;138:32. doi: 10.1038/138032a0. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
