Galectin-3 modulates Th17 responses by regulating dendritic cell cytokines
- PMID: 23916470
- PMCID: PMC3791687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.06.017
Galectin-3 modulates Th17 responses by regulating dendritic cell cytokines
Abstract
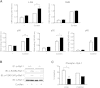
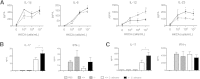
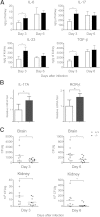
Galectin-3 is a β-galactoside-binding animal lectin with diverse functions, including regulation of T helper (Th) 1 and Th2 responses. Current data indicate that galectin-3 expressed in dendritic cells (DCs) may be contributory. Th17 cells have emerged as critical inducers of tissue inflammation in autoimmune disease and important mediators of host defense against fungal pathogens, although little is known about galectin-3 involvement in Th17 development. We investigated the role of galectin-3 in the induction of Th17 immunity in galectin-3-deficient (gal3(-/-)) and gal3(+/+) mouse bone marrow-derived DCs. We demonstrate that intracellular galectin-3 negatively regulates Th17 polarization in response to the dectin-1 agonist curdlan (a β-glucan present on the cell wall of fungal species) and lipopolysaccharide, agents that prime DCs for Th17 differentiation. On activation of dectin-1, gal3(-/-) DCs secreted higher levels of the Th17-axis cytokine IL-23 compared with gal3(+/+) DCs and contained higher levels of activated c-Rel, an NF-κB subunit that promotes IL-23 expression. Levels of active Raf-1, a kinase that participates in downstream inhibition of c-Rel binding to the IL23A promoter, were impaired in gal3(-/-) DCs. Modulation of Th17 by galectin-3 in DCs also occurred in vivo because adoptive transfer of gal3(-/-) DCs exposed to Candida albicans conferred higher Th17 responses and protection against fungal infection. We conclude that galectin-3 suppresses Th17 responses by regulating DC cytokine production.
Copyright © 2013 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

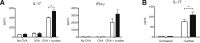
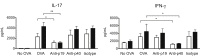

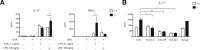



References
-
- Huang W., Na L., Fidel P.L., Schwarzenberger P. Requirement of interleukin-17A for systemic anti-Candida albicans host defense in mice. J Infect Dis. 2004;190:624–631. - PubMed
-
- Conti H.R., Shen F., Nayyar N., Stocum E., Sun J.N., Lindemann M.J., Ho A.W., Hai J.H., Yu J.J., Jung J.W., Filler S.G., Masso-Welch P., Edgerton M., Gaffen S.L. Th17 cells and IL-17 receptor signaling are essential for mucosal host defense against oral candidiasis. J Exp Med. 2009;206:299–311. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cua D.J., Sherlock J., Chen Y., Murphy C.A., Joyce B., Seymour B., Lucian L., To W., Kwan S., Churakova T., Zurawski S., Wiekowski M., Lira S.A., Gorman D., Kastelein R.A., Sedgwick J.D. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature. 2003;421:744–748. - PubMed
-
- Bettelli E., Carrier Y., Gao W., Korn T., Strom T.B., Oukka M., Weiner H.L., Kuchroo V.K. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 2006;441:235–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

