A survey on temperature-aware routing protocols in wireless body sensor networks
- PMID: 23917259
- PMCID: PMC3812583
- DOI: 10.3390/s130809860
A survey on temperature-aware routing protocols in wireless body sensor networks
Abstract
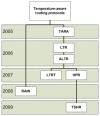
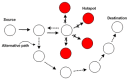
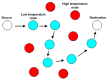
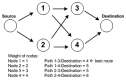
The rapid growth of the elderly population in the world and the rising cost of healthcare impose big issues for healthcare and medical monitoring. A Wireless Body Sensor Network (WBSN) is comprised of small sensor nodes attached inside, on or around a human body, the main purpose of which is to monitor the functions and surroundings of the human body. However, the heat generated by the node's circuitry and antenna could cause damage to the human tissue. Therefore, in designing a routing protocol for WBSNs, it is important to reduce the heat by incorporating temperature into the routing metric. The main contribution of this paper is to survey existing temperature-aware routing protocols that have been proposed for WBSNs. In this paper, we present a brief overview of WBSNs, review the existing routing protocols comparatively and discuss challenging open issues in the design of routing protocols.
Figures


References
-
- United Nations World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision. [(accessed on 5 March 2012)]. Available online: http://esa.un.org/wpp/
-
- IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks-Part 15.6: Wireless Body Area Networks. 2012 Feb 29;:1–271. IEEE Std 802.15.6-2012.
-
- Ullah S., Higgins H., Braem B., Latre B., Blondia C., Moerman I., Saleem S., Rahman Z., Kwak K.S. A comprehensive survey of wireless body area networks. J. Med. Syst. 2012;36:1065–1094. - PubMed
-
- Hirata A., Shiozawa T. Correlation of maximum temperature increase and peak SAR in the human head due to handset antennas. IEEE T. Microw. Theory. 2003;51:1834–1841.
-
- Havenith G. Individualized model of human thremoregulation for the simulation of heat stress response. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001;90:1943–1954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

