Retinal regeneration in adult zebrafish requires regulation of TGFβ signaling
- PMID: 23918319
- PMCID: PMC4127981
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.22549
Retinal regeneration in adult zebrafish requires regulation of TGFβ signaling
Abstract
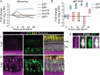
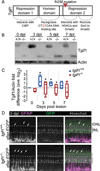
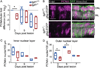
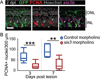
Müller glia are the resident radial glia in the vertebrate retina. The response of mammalian Müller glia to retinal damage often results in a glial scar and no functional replacement of lost neurons. Adult zebrafish Müller glia, in contrast, are considered tissue-specific stem cells that can self-renew and generate neurogenic progenitors to regenerate all retinal neurons after damage. Here, we demonstrate that regulation of TGFβ signaling by the corepressors Tgif1 and Six3b is critical for the proliferative response to photoreceptor destruction in the adult zebrafish retina. When function of these corepressors is disrupted, Müller glia and their progeny proliferate less, leading to a significant reduction in photoreceptor regeneration. Tgif1 expression and regulation of TGFβ signaling are implicated in the function of several types of stem cells, but this is the first demonstration that this regulatory network is necessary for regeneration of neurons.
Keywords: Müller glia; photoreceptor; six3b; stem cell; tgif1.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Aigner L, Bogdahn U. TGF-beta in neural stem cells and in tumors of the central nervous system. Cell Tissue Res. 2008;331:225–241. - PubMed
-
- Ando H, Kobayashi M, Tsubokawa T, Uyemura K, Furuta T, Okamoto H. Lhx2 mediates the activity of Six3 in zebrafish forebrain growth. Dev Biol. 2005;287:456–468. - PubMed
-
- Barrios-Rodiles M, Brown KR, Ozdamar B, Bose R, Liu Z, Donovan RS, Shinjo F, Liu Y, Dembowy J, Taylor IW, Luga V, Przulj N, Robinson M, Suzuki H, Hayashizaki Y, Jurisica I, Wrana JL. High-throughput mapping of a dynamic signaling network in mammalian cells. Science. 2005;307:1621–1625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

