Origin, trafficking, and intraepithelial fate of gut-tropic T cells
- PMID: 23918956
- PMCID: PMC3754871
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20122588
Origin, trafficking, and intraepithelial fate of gut-tropic T cells
Erratum in
- J Exp Med. 2013 Oct 21;210(11):2493
Abstract
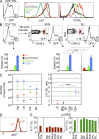
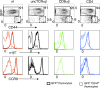
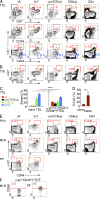
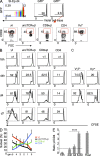
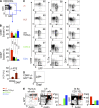
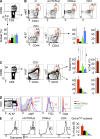
The small intestine epithelium (SI-Ep) harbors millions of unconventional (γδ and CD4(-) CD8(-) NK1.1(-) TCRαβ) and conventional (CD8αβ and CD4) T cells, designated intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs). Here, we identified the circulating pool of SI-Ep-tropic T cells and studied their capacity to colonize the SI-Ep under steady-state conditions in SPF mice. Developmentally regulated levels of α4β7 endowed recent thymic emigrants (RTEs) of unconventional types with higher SI-Ep tropism than their conventional homologues. SI-Ep-tropic RTEs, which in all lineages emerged naive, homed to the SI-Ep, but this environment was inadequate to stimulate them to cycle. In contrast, conventional and, unexpectedly, unconventional T cells, particularly Vγ7(+) (hallmark of γδ IELs), previously stimulated to cycle in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), proliferated in the SI-Ep. Cycling unconventional SI-Ep immigrants divided far more efficiently than their conventional homologues, thereby becoming predominant. This difference impacted on acquisition of high Granzyme B content, which required extensive proliferation. In conclusion, SI-Ep-tropic T cells follow a thymus-SI-Ep or a GALT-SI-Ep pathway, the latter generating highly competitive immigrants that are the sole precursors of cytotoxic IELs. These events occur continuously as part of the normal IEL dynamics.
Figures


References
-
- Arstila T., Arstila T.P., Calbo S., Selz F., Malassis-Seris M., Vassalli P., Kourilsky P., Guy-Grand D. 2000. Identical T cell clones are located within the mouse gut epithelium and lamina propia and circulate in the thoracic duct lymph. J. Exp. Med. 191:823–834 10.1084/jem.191.5.823 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

