Expression of Inflammatory Biomarkers from Cultured Sebocytes was Influenced by Treatment with Vitamin D
- PMID: 23919024
- PMCID: PMC3726901
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5154.113959
Expression of Inflammatory Biomarkers from Cultured Sebocytes was Influenced by Treatment with Vitamin D
Abstract
Background: Inflammatory cytokines are the key factor in the pathophysiology of acne. It is well known that keratinocytes synthesize many kinds of inflammatory cytokines. In addition, it is reported that inflammatory cytokines are also expressed from sebocytes, which originate from the same stem cells with keratinocytes.
Aim: To clarify changes in the expression of inflammatory biomarkers from cultured sebocytes after treatment with vitamin D.
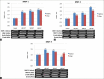
Materials and methods: Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was done to measure changes in the expression of inflammatory biomarkers, including interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and several subtypes of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) after treatment of a group of cultured sebocytes with vitamin D. Vitamin D receptor (VDR) small interfering RNA (siRNA) was added in the other group of cultured sebocytes to assure the role of vitamin D on the expression of inflammatory biomarkers. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was also performed in the vitamin D-treated sebocytes.
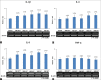
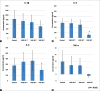
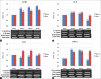
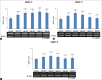
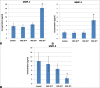
Results: Cultured sebocytes showed non-significant changes in the gene expression of inflammatory biomarkers after treatment with vitamin D. In cultured sebocytes treated with a VDR siRNA, the expression of inflammatory biomarkers was not blocked after treatment with vitamin D. ELISA showed a significant decrease in the expression of IL-6, IL-8, and MMP-9, but a significant increase in the expression of MMP-1 and MMP-3, after treatment with vitamin D (10(-6) M).
Conclusion: Expression of inflammatory biomarkers is influenced by treatment with vitamin D in cultured sebocytes, but not through VDR.
Keywords: Acne; cultured sebocyte; inflammatory cytokines; vitamin D; vitamin D siRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Winston MH, Shalita AR. Acne vulgaris. Pathogenesis and treatment. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1991;38:889–903. - PubMed
-
- Zouboulis CC. Acne and sebaceous gland function. Clin Dermatol. 2004;22:360–6. - PubMed
-
- Reichrath J. Vitamin D and the skin: An ancient friend, revisited. Exp Dermatol. 2007;16:618–25. - PubMed
-
- Lee WJ, Jung HD, Lee HJ, Kim BS, Lee SJ, Kim do W. Influence of substance-P on cultured sebocytes. Arch Dermatol Res. 2008;300:311–6. - PubMed
-
- Lee WJ, Jung HD, Chi SG, Kim BS, Lee SJ, Kim do W, et al. Effect of dihydrotestosterone on the upregulation of inflammatory cytokines in cultured sebocytes. Arch Dermatol Res. 2010;302:429–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
