L1 norm based common spatial patterns decomposition for scalp EEG BCI
- PMID: 23919646
- PMCID: PMC3750597
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-925X-12-77
L1 norm based common spatial patterns decomposition for scalp EEG BCI
Abstract
Background: Brain computer interfaces (BCI) is one of the most popular branches in biomedical engineering. It aims at constructing a communication between the disabled persons and the auxiliary equipments in order to improve the patients' life. In motor imagery (MI) based BCI, one of the popular feature extraction strategies is Common Spatial Patterns (CSP). In practical BCI situation, scalp EEG inevitably has the outlier and artifacts introduced by ocular, head motion or the loose contact of electrodes in scalp EEG recordings. Because outlier and artifacts are usually observed with large amplitude, when CSP is solved in view of L2 norm, the effect of outlier and artifacts will be exaggerated due to the imposing of square to outliers, which will finally influence the MI based BCI performance. While L1 norm will lower the outlier effects as proved in other application fields like EEG inverse problem, face recognition, etc.
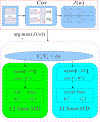
Methods: In this paper, we present a new CSP implementation using the L1 norm technique, instead of the L2 norm, to solve the eigen problem for spatial filter estimation with aim to improve the robustness of CSP to outliers. To evaluate the performance of our method, we applied our method as well as the standard CSP and the regularized CSP with Tikhonov regularization (TR-CSP), on both the peer BCI dataset with simulated outliers and the dataset from the MI BCI system developed in our group. The McNemar test is used to investigate whether the difference among the three CSPs is of statistical significance.
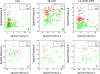
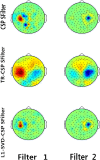
Results: The results of both the simulation and real BCI datasets consistently reveal that the proposed method has much higher classification accuracies than the conventional CSP and the TR-CSP.
Conclusions: By combining L1 norm based Eigen decomposition into Common Spatial Patterns, the proposed approach can effectively improve the robustness of BCI system to EEG outliers and thus be potential for the actual MI BCI application, where outliers are inevitably introduced into EEG recordings.
Figures
References
-
- Vaughan TM. Guest editorial brain-computer interface technology: a review of the second international meeting. Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, IEEE Transactions. 2003;11(2):94–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

