Reciprocal regulation by TLR4 and TGF-β in tumor-initiating stem-like cells
- PMID: 23921128
- PMCID: PMC3696549
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI65859
Reciprocal regulation by TLR4 and TGF-β in tumor-initiating stem-like cells
Retraction in
-
Reciprocal regulation by TLR4 and TGF-β in tumor-initiating stem-like cells.J Clin Invest. 2024 Oct 1;134(19):e186923. doi: 10.1172/JCI186923. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39352392 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
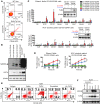
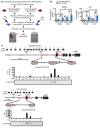
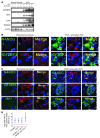
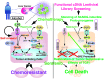
Tumor-initiating stem-like cells (TICs) are resistant to chemotherapy and associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) caused by HCV and/or alcohol-related chronic liver injury. Using HCV Tg mouse models and patients with HCC, we isolated CD133(+) TICs and identified the pluripotency marker NANOG as a direct target of TLR4, which drives the tumor-initiating activity of TICs. These TLR4/NANOG-dependent TICs were defective in the TGF-β tumor suppressor pathway. Functional oncogene screening of a TIC cDNA library identified Yap1 and Igf2bp3 as NANOG-dependent genes that inactivate TGF-β signaling. Mechanistically, we determined that YAP1 mediates cytoplasmic retention of phosphorylated SMAD3 and suppresses SMAD3 phosphorylation/activation by the IGF2BP3/AKT/mTOR pathway. Silencing of both YAP1 and IGF2BP3 restored TGF-β signaling, inhibited pluripotency genes and tumorigenesis, and abrogated chemoresistance of TICs. Mice with defective TGF-β signaling (Spnb2(+/-) mice) exhibited enhanced liver TLR4 expression and developed HCC in a TLR4-dependent manner. Taken together, these results suggest that the activated TLR4/NANOG oncogenic pathway is linked to suppression of cytostatic TGF-β signaling and could potentially serve as a therapeutic target for HCV-related HCC.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P01 CA130821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50AA11999/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- CA123328/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01AA018857/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK56338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5RC2AA019392/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AA019392/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA 014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NVRR S10/PHS HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA018857/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI83025/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24AA012885/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA123328/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI83025U19/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA108302/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AA012885/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30DK048522-13/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI083025/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048522/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA042857/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA108302/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA011999/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

