MicroRNAs in regulation of pluripotency and somatic cell reprogramming: small molecule with big impact
- PMID: 23921205
- PMCID: PMC3817145
- DOI: 10.4161/rna.25828
MicroRNAs in regulation of pluripotency and somatic cell reprogramming: small molecule with big impact
Abstract
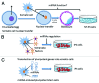
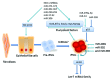
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a group of small non-coding RNAs, have emerged as significant modulators in the establishment and generation of pluripotency, a developmental process that consists of complex cell-fate arrangements. The finding of embryonic stem cell (ESC) cycle-specific miRNAs reveals an important regulation scheme of pluripotency. Subsequent studies showed the ESC-enriched or ESC-depleted miRNAs can regulate induced pluripotent stem cells(iPSC). Moreover, miRNA profiling of iPSC and ESC may distinguish them from one another and facilitate the complex of regulatory network. The accumulative effects of miRNA action enable using miRNA alone to generate iPSCs. Despite the robustness of iPSC studies, further investigations are needed since miRNA may have more impact on induced pluripotency, and the roles of miRNAs in somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), another approach toward cellular reprogramming, remains unclear. This point-of-view article will discuss miRNAs and their impact on the normal and induced pluripotency, as well as bring new insights on somatic cell reprogramming.
Keywords: MicroRNAs; embryonic stem cells; induced pluripotent stem cells; pluripotency regulation; regenerative medicine; somatic cell nuclear transfer; somatic cell reprogramming.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Frequent co-expression of miRNA-5p and -3p species and cross-targeting in induced pluripotent stem cells.Int J Med Sci. 2014 Jun 5;11(8):824-33. doi: 10.7150/ijms.8358. eCollection 2014. Int J Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24936146 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAs: important regulators of stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 May 11;8(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0551-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28494789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs in the Regulation of Pluripotency and Reprogramming.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018 Feb;14(1):58-70. doi: 10.1007/s12015-017-9782-9. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018. PMID: 29143182 Review.
-
MicroRNA-Mediated Reprogramming of Somatic Cells into Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1330:29-36. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2848-4_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26621586
-
Distinct MicroRNA Expression Signatures of Porcine Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells under Mouse and Human ESC Culture Conditions.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 6;11(7):e0158655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158655. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27384321 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Early Chondrogenesis of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (hiPSCs).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 5;20(18):4371. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184371. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31492046 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-Mediated Reprogramming of Somatic Cells into Neural Stem Cells or Neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Mar;54(2):1587-1600. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0115-9. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27660263 Review.
-
Cellular plasticity, caspases and autophagy; that which does not kill us, well, makes us different.Open Biol. 2018 Nov 28;8(11):180157. doi: 10.1098/rsob.180157. Open Biol. 2018. PMID: 30487302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Angiogenesis and Pro-Angiogenic Exosomes in Regenerative Dentistry.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 18;20(2):406. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020406. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30669338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate inflammation and pyroptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy via the miRNA-223-3p/NLRP3 pathway.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Jul 2;16(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01389-7. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38956716 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
