Spectrin domain of eukaryotic initiation factor 3a is the docking site for formation of the a:b:i:g subcomplex
- PMID: 23921387
- PMCID: PMC3784709
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.483164
Spectrin domain of eukaryotic initiation factor 3a is the docking site for formation of the a:b:i:g subcomplex
Abstract
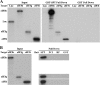
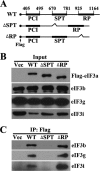
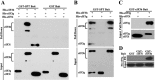
eIF3a (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3a), one of the core subunits of the eIF3 complex, has been implicated in regulating translation of different mRNAs and in tumorigenesis. A subcomplex consisting of eIF3a, eIF3b, eIF3g, and eIF3i (eIF3(a:b:i:g)) has also been identified. However, how eIF3a participates in translational regulation and in formation of the eIF3(a:b:i:g) subcomplex remain to be solved. In this study, we used the tandem affinity purification approach in combination with tandem MS/MS and identified the spectrin domain of eIF3a as the docking site for the formation of eIF3(a:b:i:g) subcomplex. Although eIF3b and eIF3i bind concurrently to the spectrin domain of eIF3a within ∼10-15 amino acids apart, eIF3g binds to eIF3a indirectly via binding to the carboxyl-terminal domain of eIF3b. The binding of eIF3b to the spectrin domain of eIF3a occurs in its RNA recognition motif domain where eIF3j also binds in a mutually exclusive manner. Together, we conclude that the spectrin domain of eIF3a is responsible for the formation of eIF3(a:b:i:g) subcomplex and, because of mutually exclusive nature of bindings of eIF3a and eIF3j to eIF3b, different subcomplexes of eIF3 likely exist and may perform noncanonical functions in translational regulation.
Keywords: Mass Spectrometry (MS); Protein-protein Interactions; Proteomics; TAP Purification; Translation Control; Translation Initiation Factors.
Figures




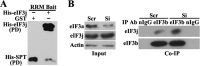

References
-
- Pestova T. V., Lorsch J. R., Hellen C. U. (2007) The mechanism of translation initiation in eukaryotes in Translational Control in Biology and Medicine (Mathews M. B., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W., eds) pp 87–128, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
-
- Dong Z., Zhang J. T. (2006) Initiation factor eIF3 and regulation of mRNA translation, cell growth, and cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 59, 169–180 - PubMed
-
- Yin J. Y., Dong Z., Liu Z. Q., Zhang J. T. (2011) Translational control gone awry: a new mechanism of tumorigenesis and novel targets of cancer treatments. Biosci. Rep. 31, 1–15 - PubMed
-
- Sun C., Todorovic A., Querol-Audí J., Bai Y., Villa N., Snyder M., Ashchyan J., Lewis C. S., Hartland A., Gradia S., Fraser C. S., Doudna J. A., Nogales E., Cate J. H. (2011) Functional reconstitution of human eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 (eIF3). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 20473–20478 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

