Bacterial division proteins FtsZ and ZipA induce vesicle shrinkage and cell membrane invagination
- PMID: 23921390
- PMCID: PMC3772209
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.491688
Bacterial division proteins FtsZ and ZipA induce vesicle shrinkage and cell membrane invagination
Abstract
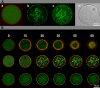
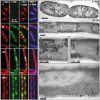
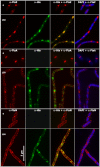
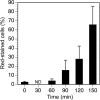
Permeable vesicles containing the proto-ring anchoring ZipA protein shrink when FtsZ, the main cell division protein, polymerizes in the presence of GTP. Shrinkage, resembling the constriction of the cytoplasmic membrane, occurs at ZipA densities higher than those found in the cell and is modulated by the dynamics of the FtsZ polymer. In vivo, an excess of ZipA generates multilayered membrane inclusions within the cytoplasm and causes the loss of the membrane function as a permeability barrier. Overproduction of ZipA at levels that block septation is accompanied by the displacement of FtsZ and two additional division proteins, FtsA and FtsN, from potential septation sites to clusters that colocalize with ZipA near the membrane. The results show that elementary constriction events mediated by defined elements involved in cell division can be evidenced both in bacteria and in vesicles.
Keywords: Bacterial Membrane; Cell Division; Escherichia coli; FtsZ; Giant Vesicles; Membrane Function; Protein-Protein Interactions; Synthetic Biology; ZipA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Escherichia coli ZipA Organizes FtsZ Polymers into Dynamic Ring-Like Protofilament Structures.mBio. 2018 Jun 19;9(3):e01008-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01008-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29921670 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-encapsulated Escherichia coli Divisome Anchor ZipA, and in Complex with FtsZ.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 10;9(1):18712. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54999-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31822696 Free PMC article.
-
A specific role for the ZipA protein in cell division: stabilization of the FtsZ protein.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 1;288(5):3219-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.434944. Epub 2012 Dec 11. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23233671 Free PMC article.
-
The FtsZ protofilament and attachment of ZipA--structural constraints on the FtsZ power stroke.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Feb;13(1):55-60. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00174-5. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11163134 Review.
-
The keepers of the ring: regulators of FtsZ assembly.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016 Jan;40(1):57-67. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv040. Epub 2015 Sep 15. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26377318 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of lipid composition and solution conditions on the mechanical properties of membrane vesicles.Membranes (Basel). 2015 Jan 20;5(1):22-47. doi: 10.3390/membranes5010022. Membranes (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25611306 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-Expressing Liposomes as Synthetic Cells for Molecular Communication Studies.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Jan 17;7:1. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00001. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30705882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On-chip microfluidic production of cell-sized liposomes.Nat Protoc. 2018 May;13(5):856-874. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2017.160. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Nat Protoc. 2018. PMID: 29599442
-
Model systems for studying cell adhesion and biomimetic actin networks.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2014 Aug 1;5:1193-202. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.5.131. eCollection 2014. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25161853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription and Translation in Cytomimetic Protocells Perform Most Efficiently at Distinct Macromolecular Crowding Conditions.ACS Synth Biol. 2020 Oct 16;9(10):2797-2807. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.0c00330. Epub 2020 Oct 5. ACS Synth Biol. 2020. PMID: 32976714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams D. W., Errington J. (2009) Bacterial cell division: assembly, maintenance and disassembly of the Z ring. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7, 642–653 - PubMed
-
- Vicente M., Rico A. I. (2006) The order of the ring: assembly of Escherichia coli cell division components. Mol. Microbiol. 61, 5–8 - PubMed
-
- Haney S. A., Glasfeld E., Hale C., Keeney D., He Z., de Boer P. (2001) Genetic analysis of the Escherichia coli FtsZ-ZipA interaction in the yeast two-hybrid system: characterization of FtsZ residues essential for the interactions with ZipA and with FtsA. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 11980–11987 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

